|
Size: 4536
Comment:
|
Size: 5135
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 11: | Line 11: |
| Ex: unpacksdcmdir -src dicomdir/subject/ALLDICOMS -targ fcMRI_dir/subject -cfg subject_config.txt -fsfast -unpackerr |
Sample cmd: |
| Line 14: | Line 13: |
| In this example command... *Have all fMRI dicoms linked into "ALLDICOMS" directory *Arguement for "-targ" specifies output directory *subject_config.txt is a configuration text file you create (format below) *Use "-fsfast" to generate fsfast hierarchy |
unpacksdcmdir -src dicomdir/subject/ALLDICOMS -targ fcMRI_dir/subject -cfg subject_config.txt -fsfast -unpackerr In this sample command... * Have all fMRI dicoms linked into "ALLDICOMS" directory * Arguement for "-targ" specifies output directory * subject_config.txt is a configuration text file you create (format below) * Use "-fsfast" to generate fsfast hierarchy |
| Line 22: | Line 24: |
| 28 bold nii f.nii 29 bold nii f.nii |
28 bold nii f.nii 29 bold nii f.nii |
| Line 25: | Line 26: |
| Col.1: scan acquisition number Col.2: output dir name will be created within "fcMRI_dir/subject" Col.3: output file format - this example is nifti format Col.4: output filename. In this example, 2 files will be created: fcMRI_dir/subject/028/f.nii fcMRI_dir/subject/029/f.nii |
Col.1: scan acquisition number Col.2: output dir name will be created within "fcMRI_dir/subject" Col.3: output file format - this example is nifti format Col.4: output filename. In this example, 2 files will be created: |
| Line 32: | Line 28: |
| 1.QA Check after unpacking: | . fcMRI_dir/subject/028/f.nii fcMRI_dir/subject/029/f.nii *QA Check after unpacking: |
| Line 36: | Line 35: |
| *STEP 2: Reconstruction Anatomical data using [[https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/recon-all| recon-all]] | *STEP 2: Reconstruction Anatomical data using [[https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/recon-all|recon-all]] |
| Line 38: | Line 37: |
| Ex: | Sample cmd: |
| Line 40: | Line 39: |
| setenv SUBJECTS_DIR /path/to/recon_dir/ recon-all -s subject_dirname -all -i pathtoT1dicom_scan1.dcm -i pathtoT1dicom_scan2.dcm |
setenv SUBJECTS_DIR /path/to/recon_dir/ recon-all -s subject_dirname -all -i pathtoT1dicom_scan1.dcm -i pathtoT1dicom_scan2.dcm |
| Line 43: | Line 41: |
| In this example command... *set your SUBJECTS_DIR variable to your FreeSurfer subject recon directory *set the subject's directory name with "-s" ... the arguement you provide will become the directory name within $SUBJECTS_DIR *use "-i" to supply the dicoms to reconstruct. Use one "-i" per T1 acquisition. 2.QA Check: |
In this sample command... * set your SUBJECTS_DIR variable to your FreeSurfer subject recon directory * set the subject's directory name with "-s" ... the arguement you provide will become the directory name within $SUBJECTS_DIR * use "-i" to supply the dicoms to reconstruct. Use one "-i" per T1 acquisition. A. QA Check: |
| Line 52: | Line 52: |
| * D - Check hierarchy of reconstructed anatomical data | * D - Check hierarchy of reconstructed anatomical data |
| Line 54: | Line 54: |
1.Double-check for FSFAST basic hierarchy |
B. Use FSFAST basic hierarch: |
| Line 59: | Line 58: |
| 2.Link to FreeSurfer anatomical analysis: | C. Link to FreeSurfer anatomical analysis: Create "subjectname" text file in the session directory. Write in it the subject's recon directory name (as labeld in $SUBJECTS_DIR). |
| Line 61: | Line 60: |
| A - Create "subjectname" text file in the session directory. Write in it the subject's recon directory name (found within $SUBJECTS_DIR). 3.Create a sessid file (text file with list of your sessions)in your Study DIR. |
D. Create a sessid file (text file with list of your sessions)in your Study DIR (optional) |
| Line 68: | Line 64: |
| Sample cmd: |
|
| Line 70: | Line 68: |
| 1.By default this will do motion correction, smoothing & brain masking | A. By default this will do motion correction, smoothing & brain masking |
| Line 72: | Line 70: |
| 2.Quality Check (plot-twf-sess) 3.Examine additions to FSFAST hierarchy (in each run of bold dir): | B. Quality Check (plot-twf-sess) |
| Line 74: | Line 72: |
| ||f.nii || (Raw fMRI data) || ||fmc.nii || (Motion corrected-MC)|| ||fmcsm5.nii|| (MC & smoothed)|| ||fmc.mcdat|| (Text file with the MC parameters (AFNI))|| ||brain.mgz ||(Binary mask of the brain)|| |
C.Examine additions to FSFAST hierarchy (in each run of bold dir): |
| Line 80: | Line 74: |
| # Function-Structure Registration View unregistered: | ||f.nii ||(Raw fMRI data) || ||fmc.nii ||(Motion corrected-MC) || ||fmcsm5.nii ||(MC & smoothed) || ||fmc.mcdat ||(Text file with the MC parameters (AFNI)) || ||brain.mgz ||(Binary mask of the brain) || |
| Line 82: | Line 80: |
| . [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/tkregister-sess|tkregister-sess]] -s <subjid> -regheader) | |
| Line 84: | Line 81: |
| Run automatic registration: . [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/spmregister-sess|spmregister-sess]] -s <subjid> Check automatic registration: . [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/tkregister-sess|tkregister-sess]] -s <subjid> A - Make edits if needed using scale as the last resort Check talairach registration: . [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/tkregister2|tkregister2]] --s <subjid> --fstal --surf |
|
| Line 98: | Line 84: |
| This example will use the FreeSurfer cortical segmentation for the left posterior cingulate (segID: 1010). For seed regions, we recommend generating the mean signal timecourse by using "-mean" Sample cmd (mean seed region timecourse): fcseed-sess -segid 1010 -o mean.L_Posteriorcingulate.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -mean Sample cmd (Principal component analysis for nuisance regressors): for white matter: fcseed-sess -wm -o wm.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -pca for ventricles + CSF: fcseed-sess -vcsf -o vcsf.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -pca |
|
| Line 100: | Line 102: |
| *STEP 6: Use [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/selxavg3-sess|selxavg3-sess]] to run the subject-level analysis | Sample cmd: |
| Line 102: | Line 104: |
| *STEP 7: Use [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/mri_glmfit|mri_glmfit]] or [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/selxavg3-sess|selxavg3-sess]] to run a group-level analysis | mkanalysis-sess -a <AnalysisName> -surface fsaverage <hemi> -notask -taskreg mean.L_Posteriorcingulate.dat 1 -nuisreg vcsfreg.dat 3 -nuisreg wmreg.dat 3 -nuisreg global.waveform.dat 1 -fwhm 5 -fsd bold -TR <TR> -mcextreg -polyfit 2 -nskip 4 *STEP 6: Use [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/selxavg3-sess|selxavg3-sess]] to run the subject-level analysis outlined by the above mkanalysis-sess cmd. selxavg3-sess -s <session> -a <AnalysisName> *STEP 7: Use [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/mri_glmfit|mri_glmfit]]or [[http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/selxavg3-sess|selxavg3-sess]]to run a group-level analysis |
work in progress...
About
Walkthrough: How to use FsFast and fcseed-sess for functional connectivity analysis including example commands.
For general tips on using FsFast, download this FS-FAST powerpoint
This walkthrough demonstrates how to run a functional connectivity analysis on resting state fMRI data.
*STEP 1: Unpack Data into the FSFAST Hierarchy using unpacksdcmdir
Sample cmd:
unpacksdcmdir -src dicomdir/subject/ALLDICOMS -targ fcMRI_dir/subject -cfg subject_config.txt -fsfast -unpackerr
In this sample command...
- Have all fMRI dicoms linked into "ALLDICOMS" directory
- Arguement for "-targ" specifies output directory
- subject_config.txt is a configuration text file you create (format below)
- Use "-fsfast" to generate fsfast hierarchy
subject_config.txt format:
28 bold nii f.nii 29 bold nii f.nii
Col.1: scan acquisition number Col.2: output dir name will be created within "fcMRI_dir/subject" Col.3: output file format - this example is nifti format Col.4: output filename. In this example, 2 files will be created:
- fcMRI_dir/subject/028/f.nii fcMRI_dir/subject/029/f.nii
*QA Check after unpacking:
- A - Check unpacked data (time points, # of slices ..etc)
- B - Check FSFAST hierarchy in session folder
*STEP 2: Reconstruction Anatomical data using recon-all
Sample cmd:
setenv SUBJECTS_DIR /path/to/recon_dir/ recon-all -s subject_dirname -all -i pathtoT1dicom_scan1.dcm -i pathtoT1dicom_scan2.dcm
In this sample command...
set your SUBJECTS_DIR variable to your FreeSurfer subject recon directory
- set the subject's directory name with "-s" ... the arguement you provide will become the directory name within $SUBJECTS_DIR
- use "-i" to supply the dicoms to reconstruct. Use one "-i" per T1 acquisition.
A. QA Check:
- A - Check talairach transformation
B - Check skull strip, white matter & pial surface
- C - Re-run "recon-all" if edits are made
- D - Check hierarchy of reconstructed anatomical data
B. Use FSFAST basic hierarch:
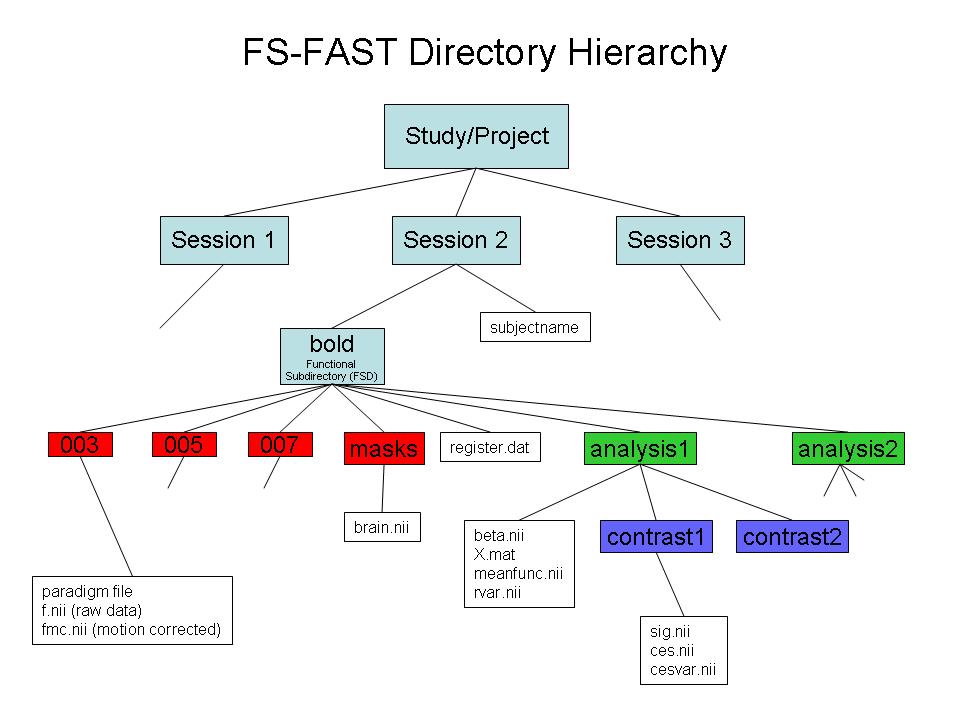
C. Link to FreeSurfer anatomical analysis: Create "subjectname" text file in the session directory. Write in it the subject's recon directory name (as labeld in $SUBJECTS_DIR).
D. Create a sessid file (text file with list of your sessions)in your Study DIR (optional)
*STEP 3: Pre-process your bold data using preproc-sess preproc-sess
Sample cmd:
preproc-sess -s <subjid> -fwhm <#>
A. By default this will do motion correction, smoothing & brain masking
B. Quality Check (plot-twf-sess)
C.Examine additions to FSFAST hierarchy (in each run of bold dir):
f.nii
(Raw fMRI data)
fmc.nii
(Motion corrected-MC)
fmcsm5.nii
(MC & smoothed)
fmc.mcdat
(Text file with the MC parameters (AFNI))
brain.mgz
(Binary mask of the brain)
*STEP 4: Use fcseed-sess to generate time-course information for your chosen seed region (as well as nuisance variable signal).
This example will use the FreeSurfer cortical segmentation for the left posterior cingulate (segID: 1010). For seed regions, we recommend generating the mean signal timecourse by using "-mean"
Sample cmd (mean seed region timecourse):
fcseed-sess -segid 1010 -o mean.L_Posteriorcingulate.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -mean
Sample cmd (Principal component analysis for nuisance regressors):
for white matter:
fcseed-sess -wm -o wm.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -pca
for ventricles + CSF:
fcseed-sess -vcsf -o vcsf.dat -s <session> -fsd bold -pca
*STEP 5: Use mkanalysis-sess to setup an analysis for your FC data
Sample cmd:
mkanalysis-sess -a <AnalysisName>
-surface fsaverage <hemi> -notask -taskreg mean.L_Posteriorcingulate.dat 1 -nuisreg vcsfreg.dat 3 -nuisreg wmreg.dat 3 -nuisreg global.waveform.dat 1 -fwhm 5 -fsd bold -TR <TR> -mcextreg -polyfit 2 -nskip 4
*STEP 6: Use selxavg3-sess to run the subject-level analysis outlined by the above mkanalysis-sess cmd.
selxavg3-sess -s <session> -a <AnalysisName>
*STEP 7: Use
selxavg3-sessto run a group-level analysis
