| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 56: | Line 56: |
| * ''samseg.stats'': contains the estimated volume (in cubic mm) for each segmented structure. These volumes will be very close (but not identical to) the number of voxels assigned to each structure in "seg.mgz" -- the reason for the discrepancy is that "seg.mgz" is computed in a winner-takes-all fashion, ignoring the uncertainty about the underlying voxel assignments. | * ''samseg.stats'': contains the estimated volume (in cubic mm) for each segmented structure. These volumes will be very close (but not identical to) the number of voxels assigned to each structure in "seg.mgz" -- the reason for the discrepancy is that "seg.mgz" is computed in a winner-takes-all fashion, ignoring the uncertainty about the underlying voxel assignments (and therefore slightly less accurate). |
This page is readable only by those in the LcnGroup and CmetGroup.
Samseg (cross-sectional, longitudinal, MS lesions)
This functionality is available in FreeSurfer 7, with gradual improvements appearing in the development version.
Author: Koen Van Leemput
E-mail: koen [at] nmr.mgh.harvard.edu
Rather than directly contacting the author, please post your questions on this module to the FreeSurfer mailing list at freesurfer [at] nmr.mgh.harvard.edu
If you use these tools in your analysis, please cite:
Cross-sectional: Fast and sequence-adaptive whole-brain segmentation using parametric Bayesian modeling. O. Puonti, J.E. Iglesias, K. Van Leemput. Neuroimage, 143, 235-249, 2016.
Longitudinal: A Longitudinal Method for Simultaneous Whole-Brain and Lesion Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis. S. Cerri, A. Hoopes, D.N. Greve, M. Mühlau, K. Van Leemput. International Workshop on Machine Learning in Neuroimaging, 2020.
MS lesions: A Contrast-Adaptive Method for Simultaneous Whole-Brain and Lesion Segmentation in Multiple Sclerosis. S. Cerri, O. Puonti, D.S. Meier, J. Wuerfel, M. Mühlau, H.R. Siebner, K. Van Leemput. 2020.
See also: ThalamicNuclei, HippocampalSubfieldsAndNucleiOfAmygdala, BrainstemSubstructures
1. General Description
Sequence Adaptive Multimodal SEGmentation (SAMSEG) is a tool to robustly segment dozens of brain structures from head MRI scans without preprocessing. The characteristic property of SAMSEG is that it accepts multi-contrast MRI data without prior assumptions on the specific type of scanner or pulse sequences used. Dedicated versions to handle longitudinal data, or to segment white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients are also available.
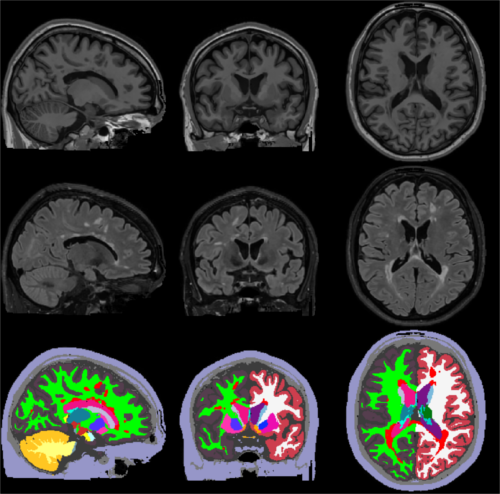
The figure below illustrates a typical SAMSEG segmentation result on a T1w-FLAIR scan of a MS patient:
2. Basic SAMSEG (cross-sectional processing)
In its most basic form SAMSEG takes one or more co-registered MRI volumes as input, and produces an output segmentation in around 10 min on a good desktop computer (with multi-threading enabled). Preprocessing of the scan(s) with FreeSurfer is neither required nor recommended (e.g., no reformatting to 1mm isotropic resolution, no bias field correction and no skull stripping is needed nor recommended). The command line is:
run_samseg --input <file> [<file> ...] --output <dir> [--threads <threads>] [--pallidum-separate]
where:
<file>: is the path to the input volume(s) in Nifti (.nii/.nii.gz) or FreeSurfer (.mgz) file format. If you have more than one contrast (e.g., both T1w and T2w) you can simply list all the input contrasts you want to use -- the only requirement is that all input volumes are co-registered with each other, and have the same image grid size and voxel dimensions (see below for instructions on how to do that with FreeSurfer).
<dir>: is the path to the output directory where the results will be saved. If this directory doesn't exist, it will be created automatically.
<threads> (optional): is the number of threads to be used by SAMSEG (default uses one thread). Set the number of threads to the number of CPU cores on your computer to get the fastest run time.
--pallidum-separate (optional): by default SAMSEG will treat the pallidum internally as a white matter structure, since it typically can't be discerned easily from white matter in T1w scans. However, if your combination of input volumes includes contrasts where the pallidum is clearly discernible (e.g., T2w or FLAIR) you should add this flag to your command line.
The output will consist of the following set of files, which can be found under the specified <dir> directory:
seg.mgz: is the output segmentation volume, where each voxel has been assigned to one anatomical structure. This file is similar to the "aseg.mgz" file produced by the standard volumetric stream in FreeSurfer: the correspondence between structure numbers and neuroanatomical labels is according to $FREESURFER_HOME/FreeSurferColorLUT.txt.
samseg.stats: contains the estimated volume (in cubic mm) for each segmented structure. These volumes will be very close (but not identical to) the number of voxels assigned to each structure in "seg.mgz" -- the reason for the discrepancy is that "seg.mgz" is computed in a winner-takes-all fashion, ignoring the uncertainty about the underlying voxel assignments (and therefore slightly less accurate).
Co-registering multi-contrast data:
XXX
Examples:
Segment a single scan:
mri_segment_hypothalamic_subunits --i /home/user1/data/scan.mgz --o home/user1/data/seg.mgz
