| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| <<BR>>The course specific instructions are after the general information, starting with the detailed Windows and Mac downloading instructions. The general information will likely not be helpful, as this course uses simplified methods of downloading and verifying FreeSurfer. | <<BR>>The online course specific instructions are at the page CourseInstructions as they are significantly different. |
FreeSurfer VirtualBox VM Images
FREESURFER COURSE INFO:
The online course specific instructions are at the page CourseInstructions as they are significantly different.
System Requirements:
Tested running on hosts: Windows 10, Mac OS 11.6 (Intel Mac) with VirtualBox 6.1.30.
VM: minimum of 8 GB free RAM apart from RAM already in use by the host OS and other applications.
VM: minimum of 2 CPU's/cores from the host.
Host Graphics card: 3D graphics card with its own graphics memory & accelerated OpenGL drivers.
Host Disk Space (required): ~8GB for virtual image download (compressed *.ova file), ~30G for expanded VM image.*
Host Disk Space (optional): ~8GB for tutorial data download (compressed *.tgz file), ~14G for expanded tutorial data.*
Host: A working network connection.
Additionally see the Freesurfer Release 7 System Requirements.
* To accommodate the VM, the tutorial data, and other data, please locate the VM on a disk partition with at least 60G of free space.
Suggested Experience Level:
Some familiarity with downloading files, e.g., via a web browser or using commands such as wget, curl from the linux terminal.
Some familiarity with the linux terminal running bash shell including removing, copying, editing files and setting/unsetting environment variables.
Some familiarity with simple bash commands/scripting, e.g., as found in the shell initialization file.
Install VirtualBox on your Host Machine:
VirtualBox install on Windows OS host: Vbox_Windows_install.pdf
VirtualBox install on MacOS host: Vbox_MacOS_install.pdf *
VirtualBox install on linux OS host: linux downloads
* We are aware that VirtualBox may crash on Intel or M1 Macs running MacOS 12.x (Monterey).
Download and Run the Virtual Machine:
Ubuntu 18.04.06 compressed image with the FreeSurfer 7.2.0 release installed: FS_7_2_0_Ubuntu_18_04_06.ova.7z
Right click on the <file name>.ova.7z file and see what options you have under the choices for "Open with". If your current archive program choices cannot open a 7zip file, then try installing one of the utilities listed below. You will be prompted for a pass code when the archive is successfully opened. If you do not have the pass code to open the image, then send an email to the FreeSurfer help list to receive it.
For 7zip on Windows try the free version of WinRAR to expand the 7zip file.
For 7zip on MacOS try the free Unarchiver to expand the 7zip file.
For 7zip on linux try the package manager programs, e.g., yum, dnf, apt, to download and install a 7z or 7za binary.
Expanding the <file name>.ova.7z will generate a new file without the .7z extension, i.e., <file name>.ova will be created. This is the file to import directly into VirtualBox. If the archive program creates the <file name>.ova file under a subdirectory with the same <file name>.ova name, then rename the subdirectory to be something different. Be aware that some archive programs may delete the original <file name>.ova.7z file after it is expanded.
This document will take you through the steps to setup and run the VM. Screenshots to setup the VM were taken from VirtualBox running on MacOS and Windows. Apart from some variations in the GUI on different hosts, the menus options are the same on MacOS, Windows and Linux. See: Vbox_load_image.pdf
See this post about how to share a subdirectory from Windows inside the Ubuntu VM.
This document describes how to access (share) an external drive plugged into the Windows machine in the Ubuntu VM:
Vbox_Windows_mount_external_drive.pdf
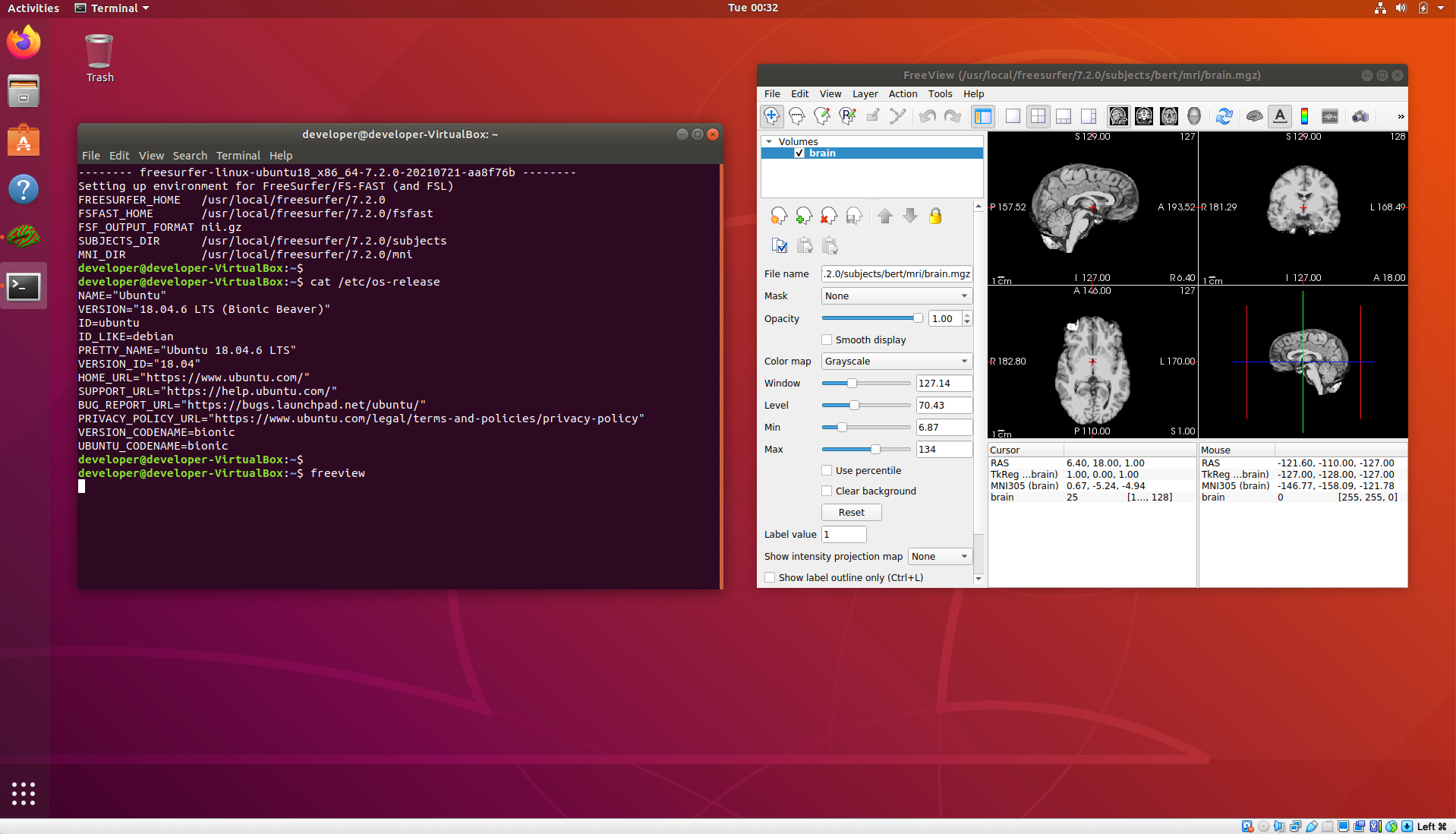
Example screenshot of VM up and running:
Once the VM starts and you have added your FreeSurfer license file, you can start a terminal and it should come up with the environment set to run the 7.2.0 release.
Adding the tutorial data to the VM:
This document describes how to setup, run and test the VM using commands from the FreeSurfer course tutorial data; the primary focus is on the Freeview command.
setup_tutorial_data.pdf
FreeSurfer Course Installation Instructions
Downloading & Installing Virtualbox
The first step in getting ready for the FreeSurfer Course is downloading VirtualBox. It is a virtual machine software, able to easily replicate the environment and user interface of another computer, in this case one with FreeSurfer preinstalled. First you will need to download the file that contains the Image (more information forthcoming), and then follow the instructions on how to set up the virtual machine. These steps differ for MacOS and Windows, so instructions for both are below. Make sure to download the tutorial data as well; instructions on tutorial data is bellow install instructions.
Installing On Windows
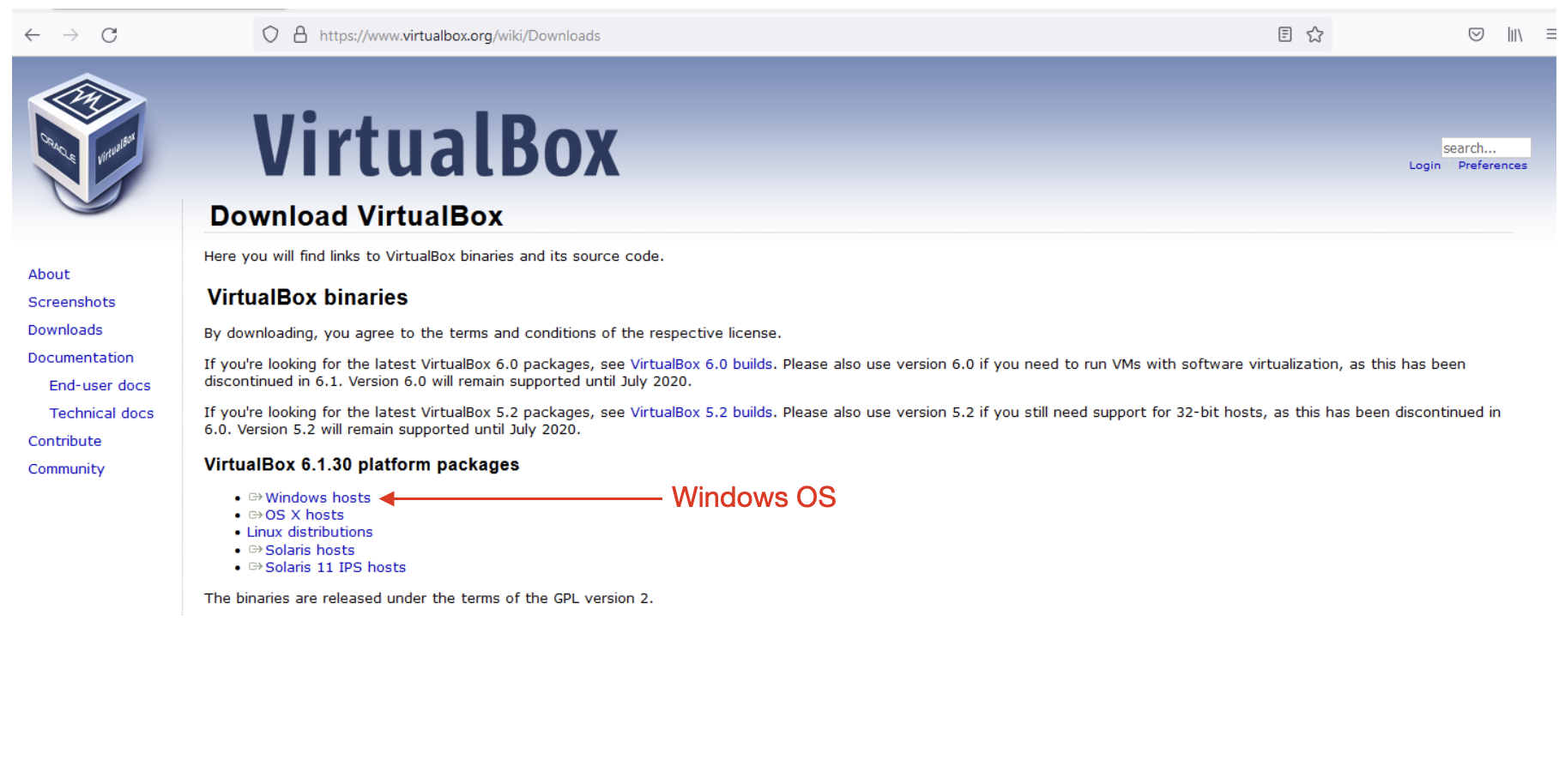
1. Navigate to the VirtualBox website, https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads, and download the latest version of VirtualBox.
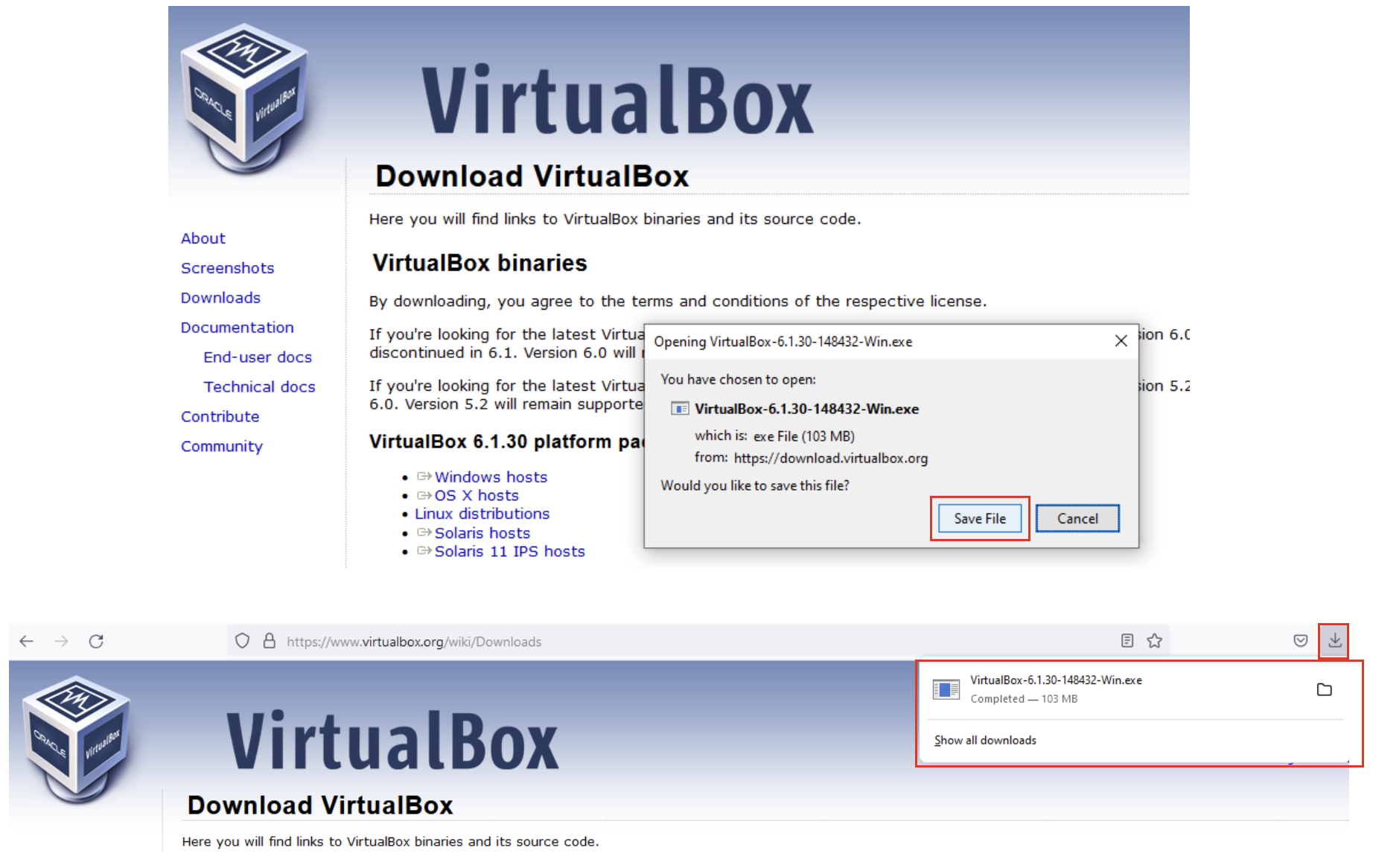
2. Save the installer and wait for the download to finish.
3. Locate the installer in the Downloads folder and double click on it to launch it.
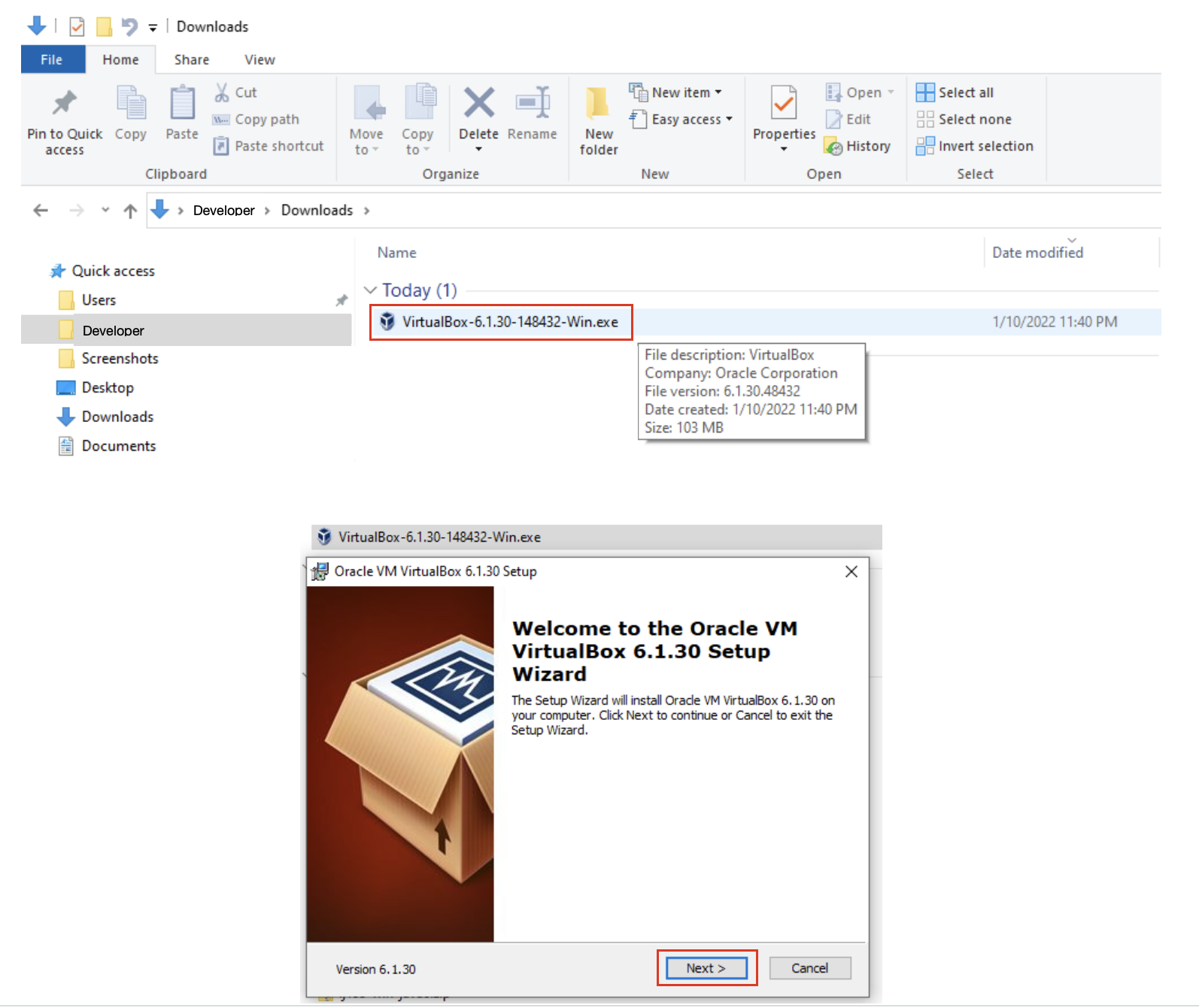
4. Choose to install the default setup/configuration with the default options
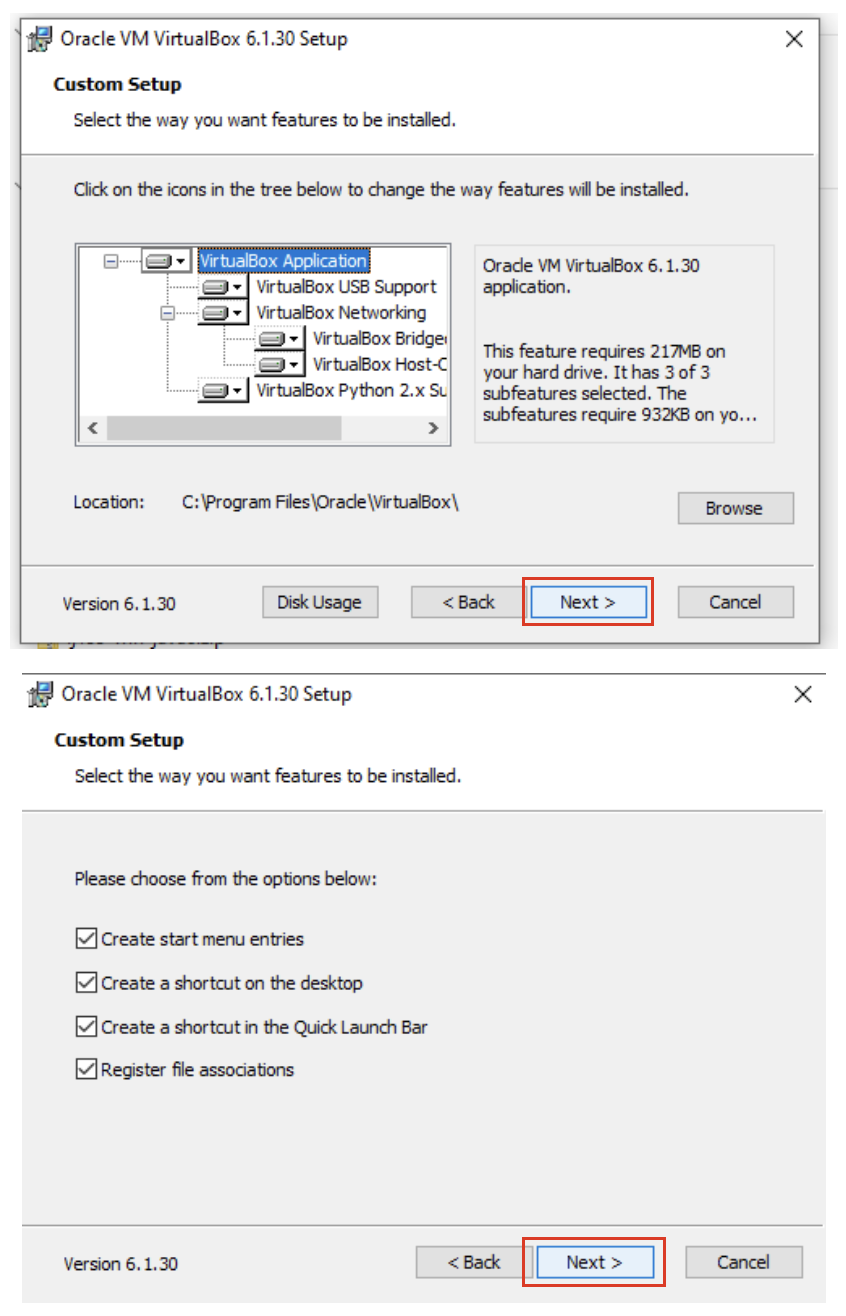
5. Allow the network connection to be reset and start the installation.
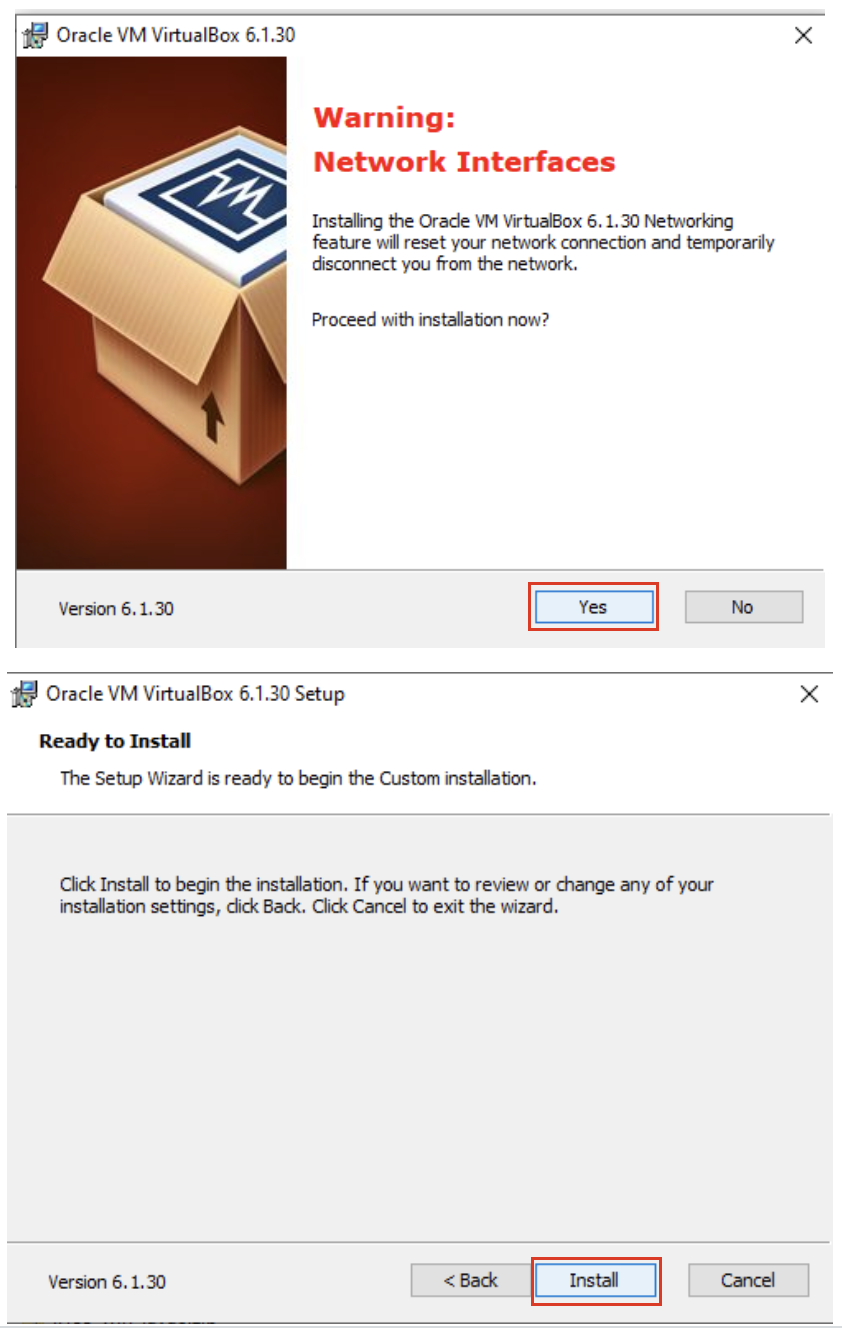
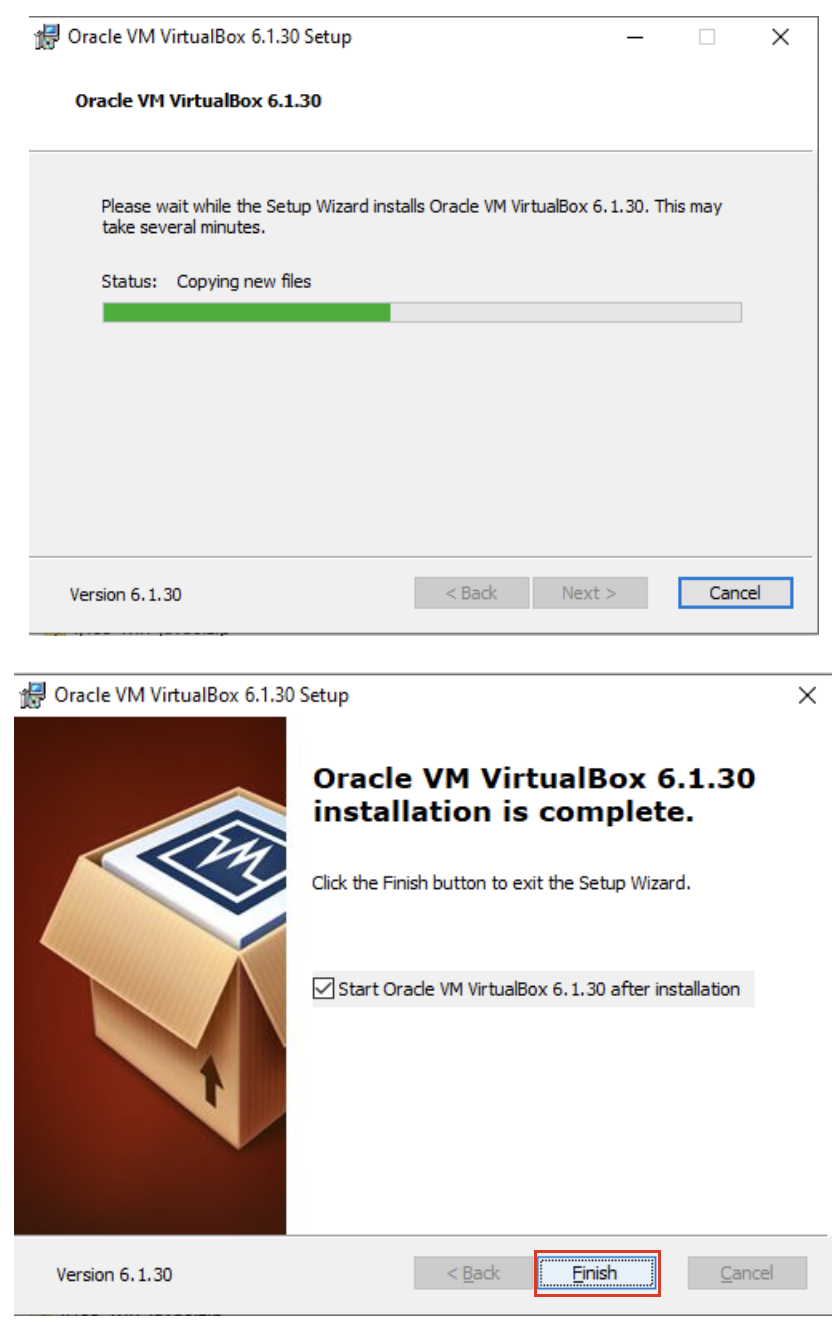
6. Allow the installation to progress and complete. Then click the finish button.
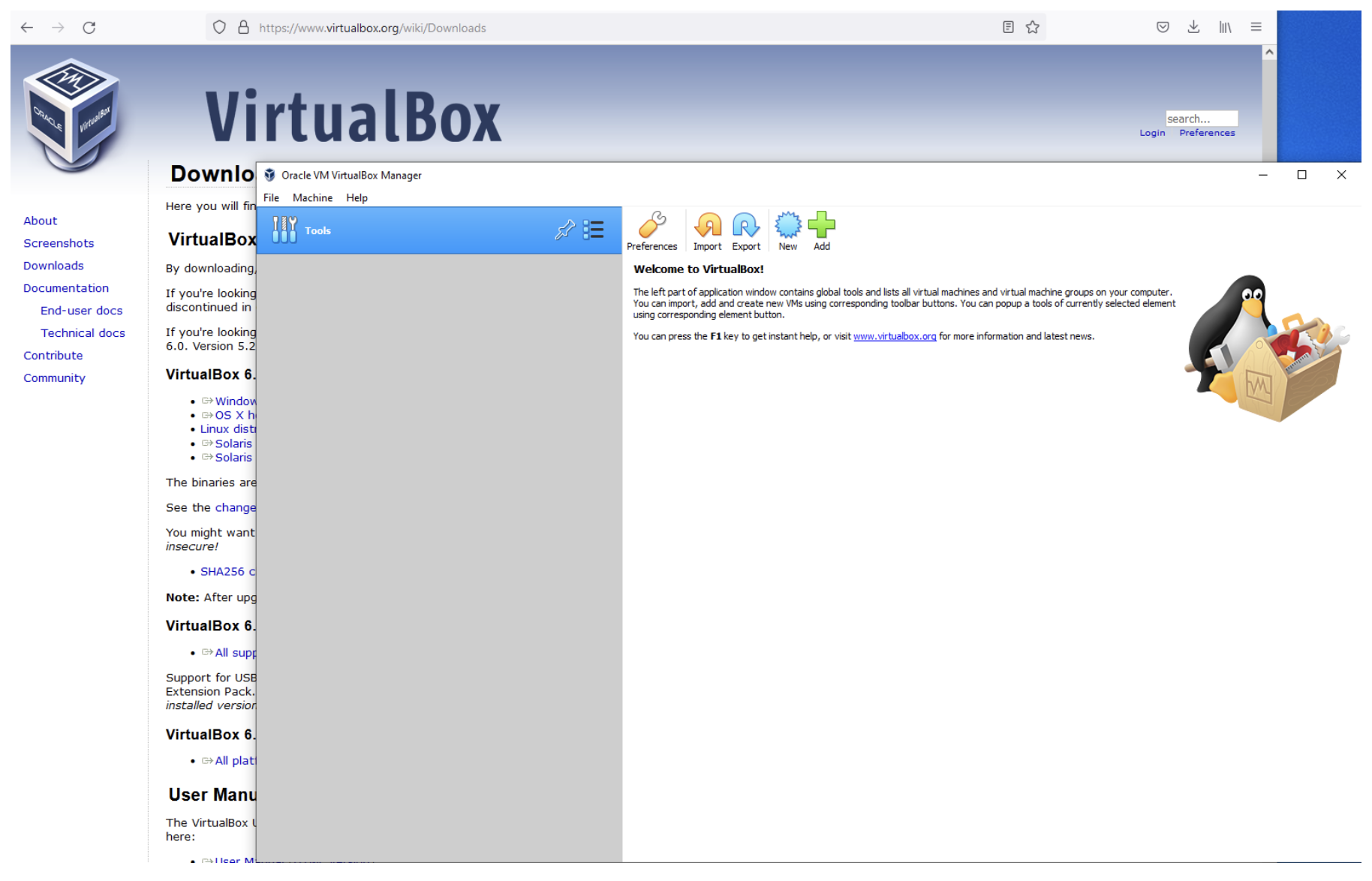
7. VirtualBox should automatically launch and display an empty window (containing no virtual machines).
Installing on MacOS
Reminder: Any ARM based computers, including M1 and M2 Macs, will not work with VirtualBox, or our planned course.
1. Navigate to the VirtualBox website, https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads, and download the latest version of VirtualBox.
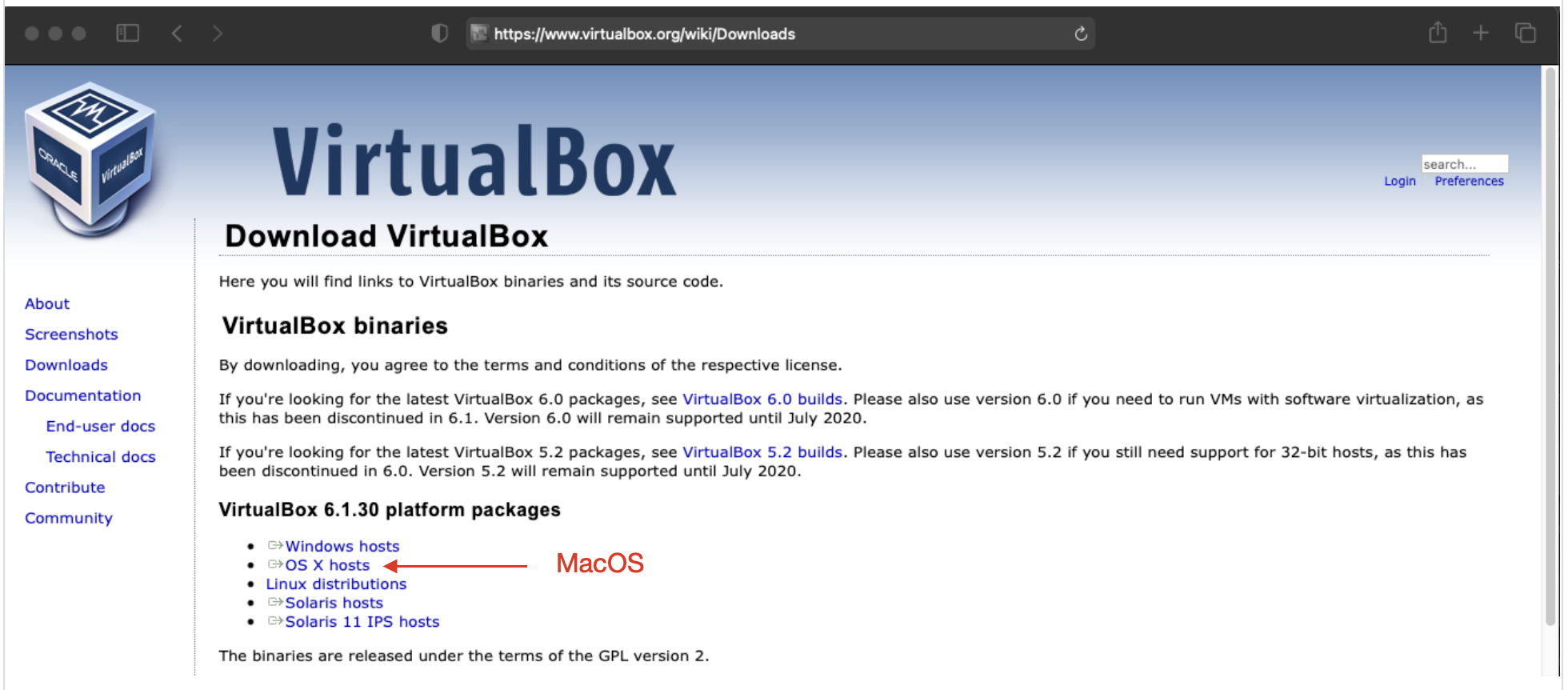
2. Allow downloads from the VirtualBox web site.
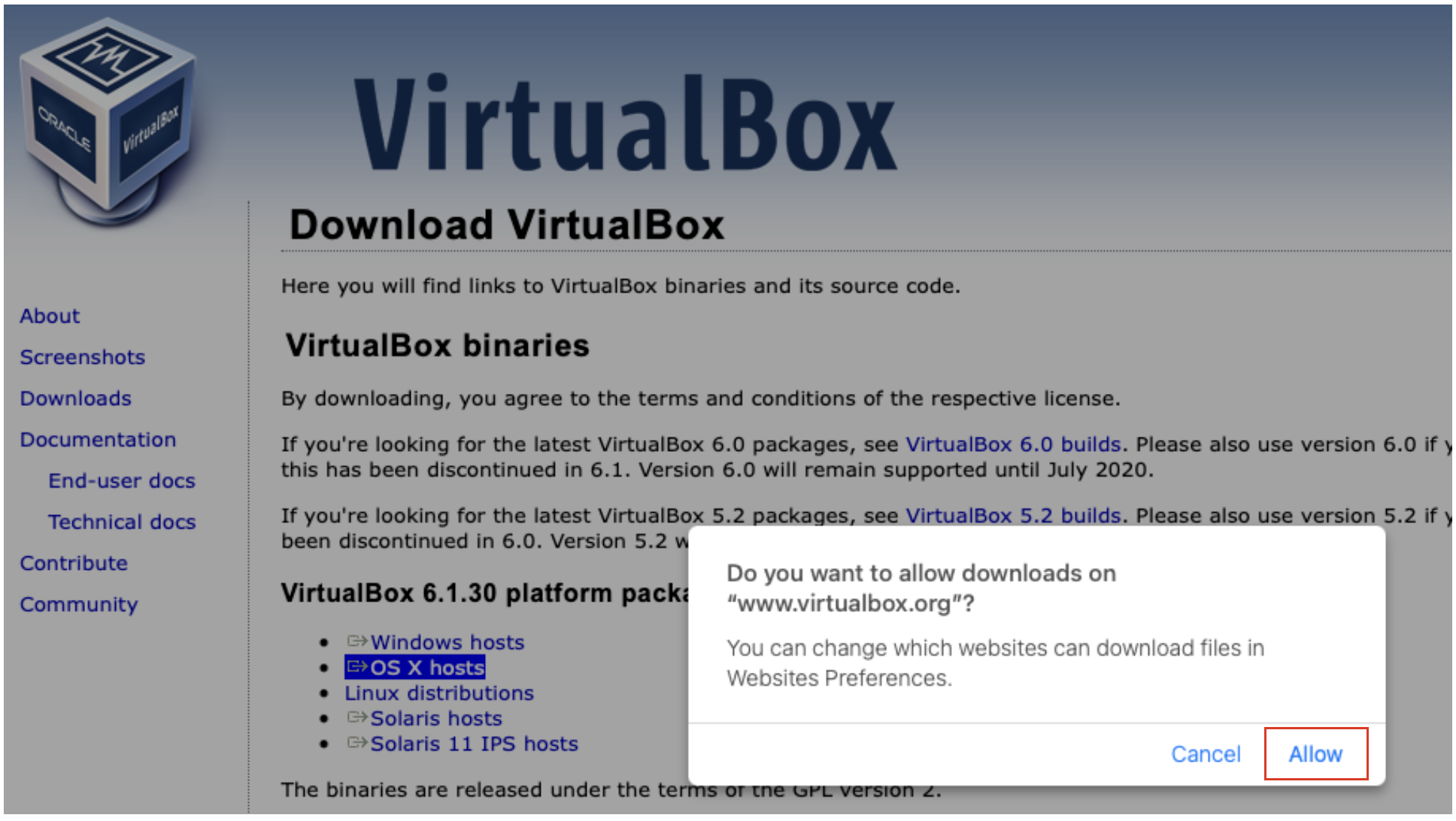
3. Open the download archive when it finishes.
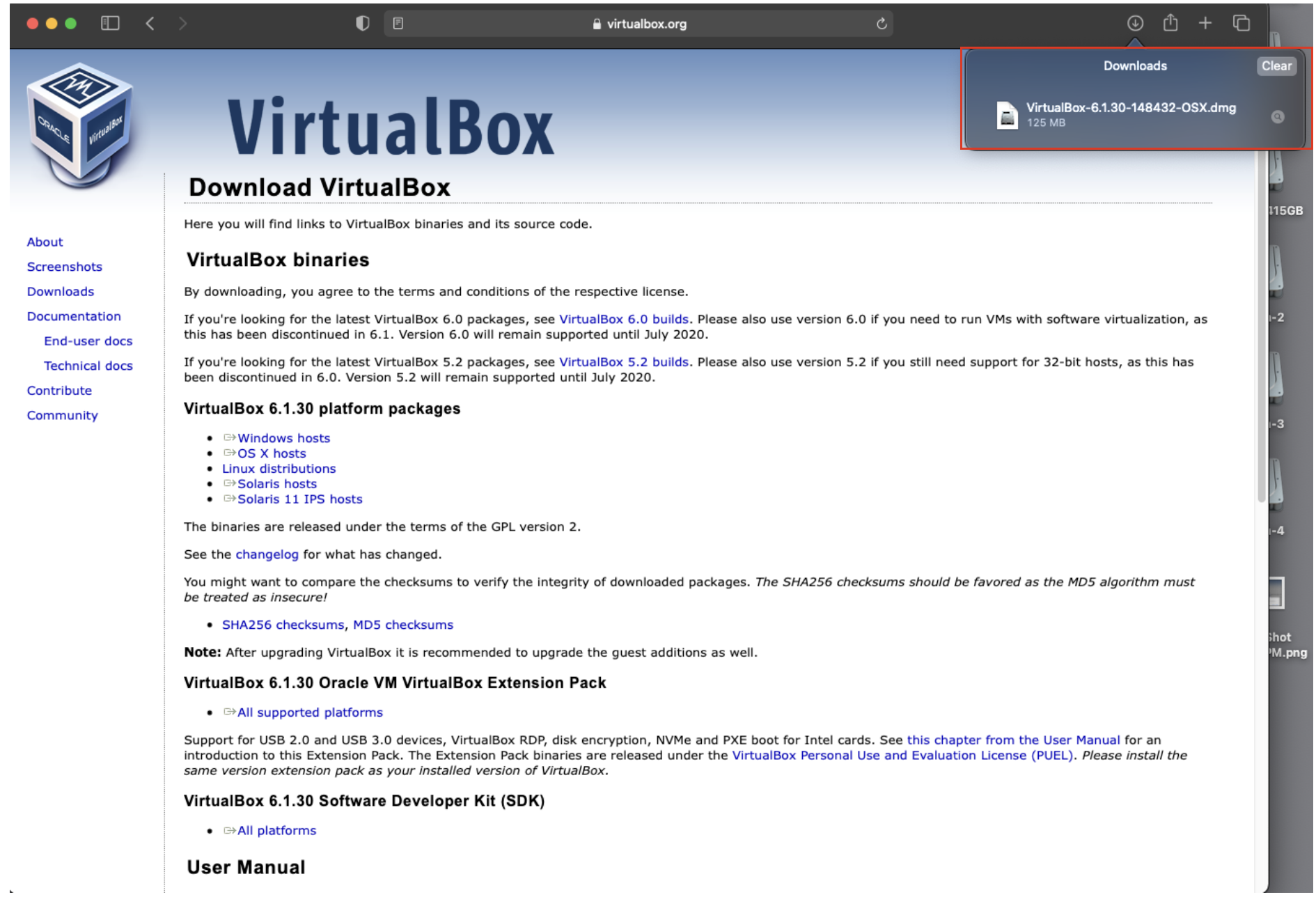
4. Double click on the VirtualBox package installer
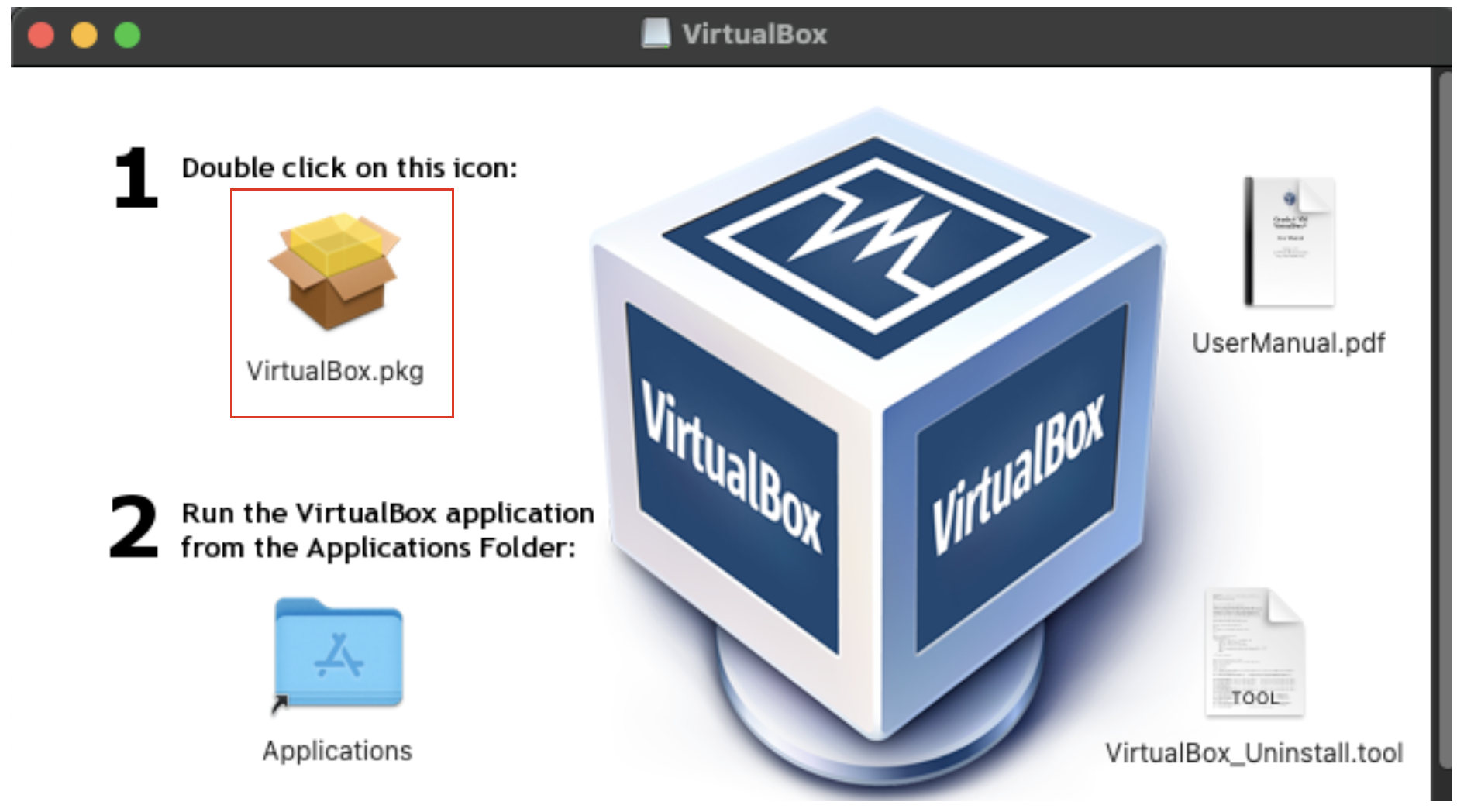
5. Give the installer permission to run scripts.
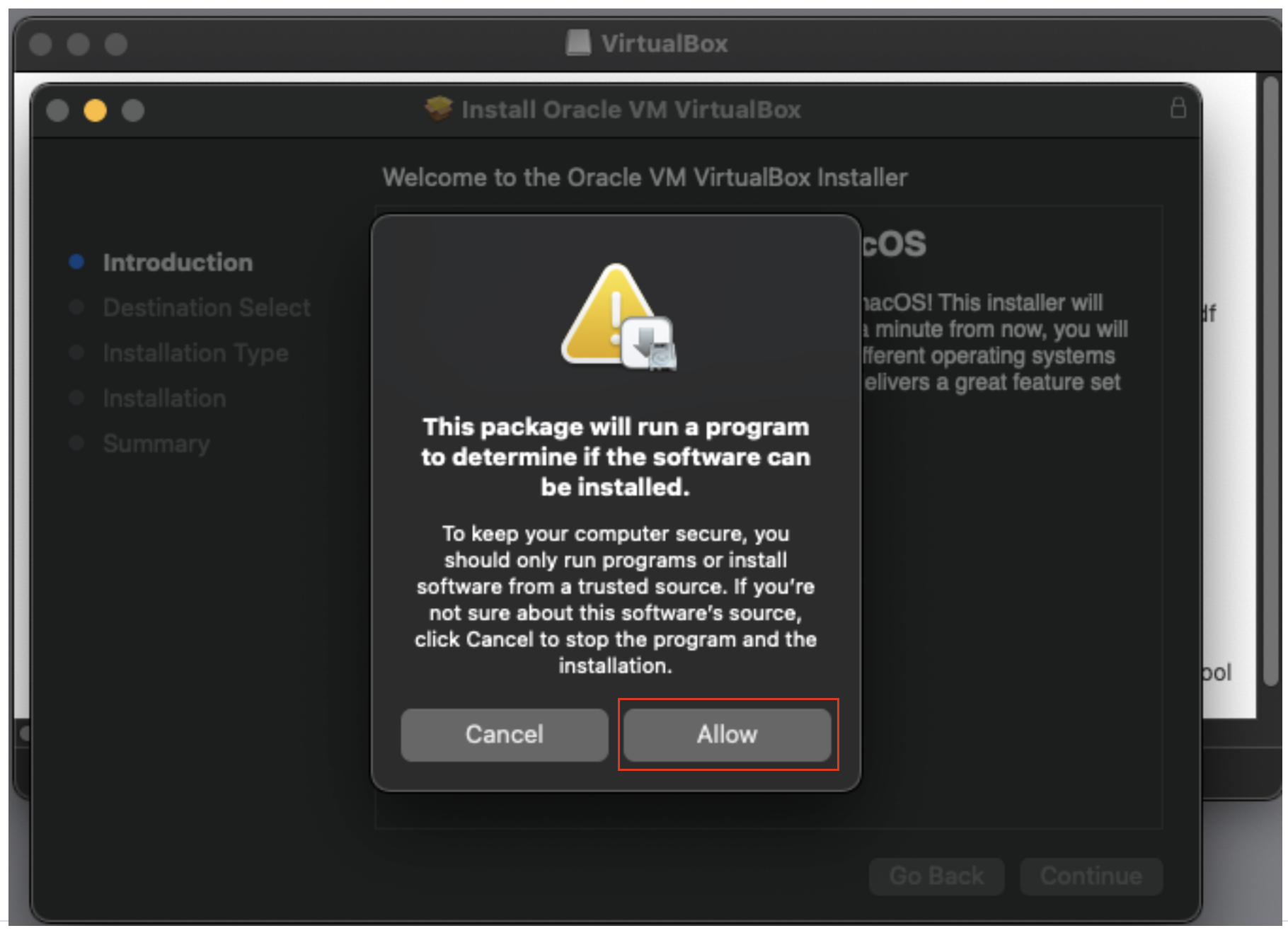
6. Allow the installer to continue.
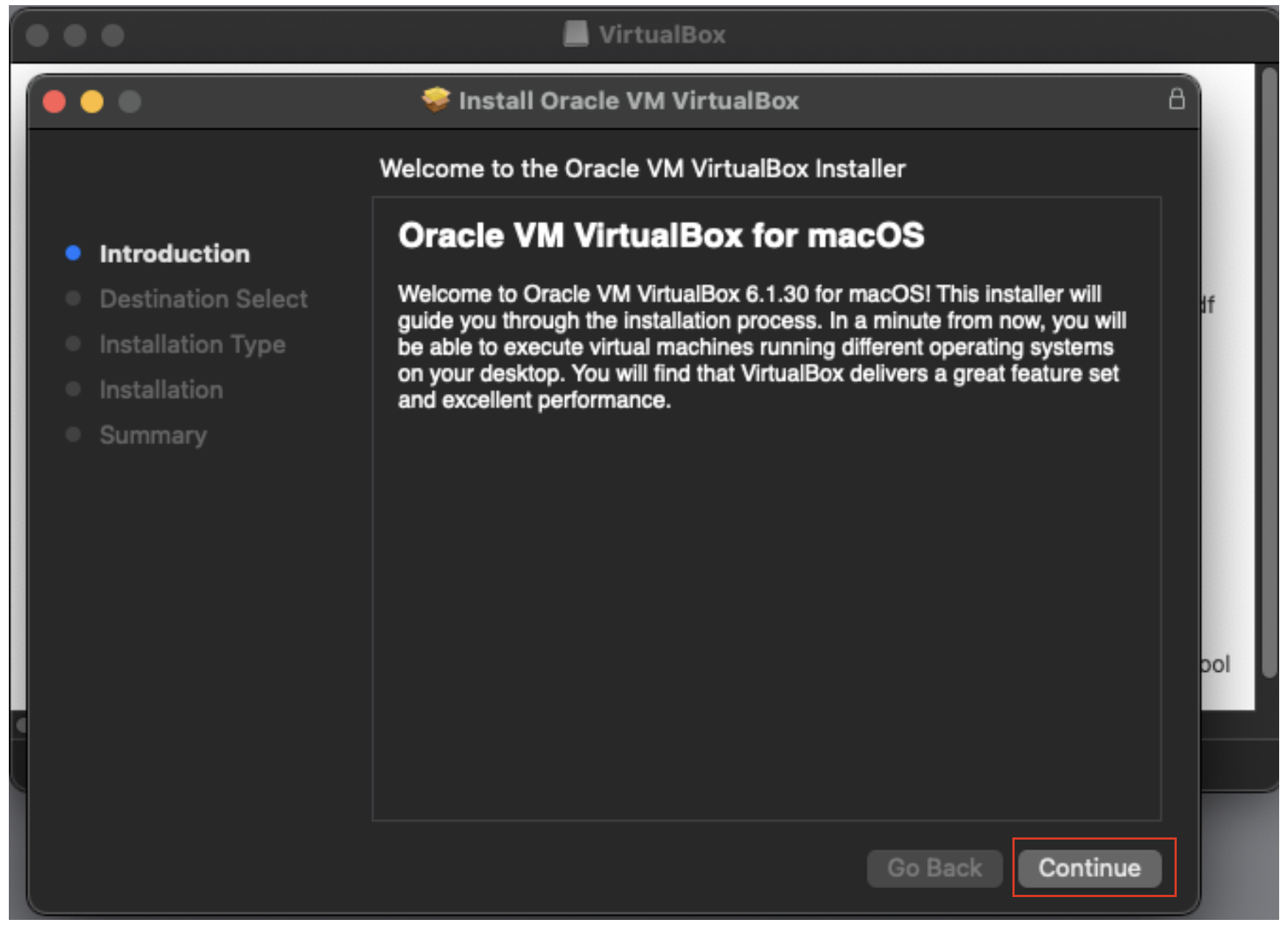
7. Pick a destination for the VirtualBox application. The default install location in the Applications folder on the boot partition should be fine (here an external disk named “external_BigSur)”. Your boot partition will be named differently, e.g., Macintosh HD, etc.
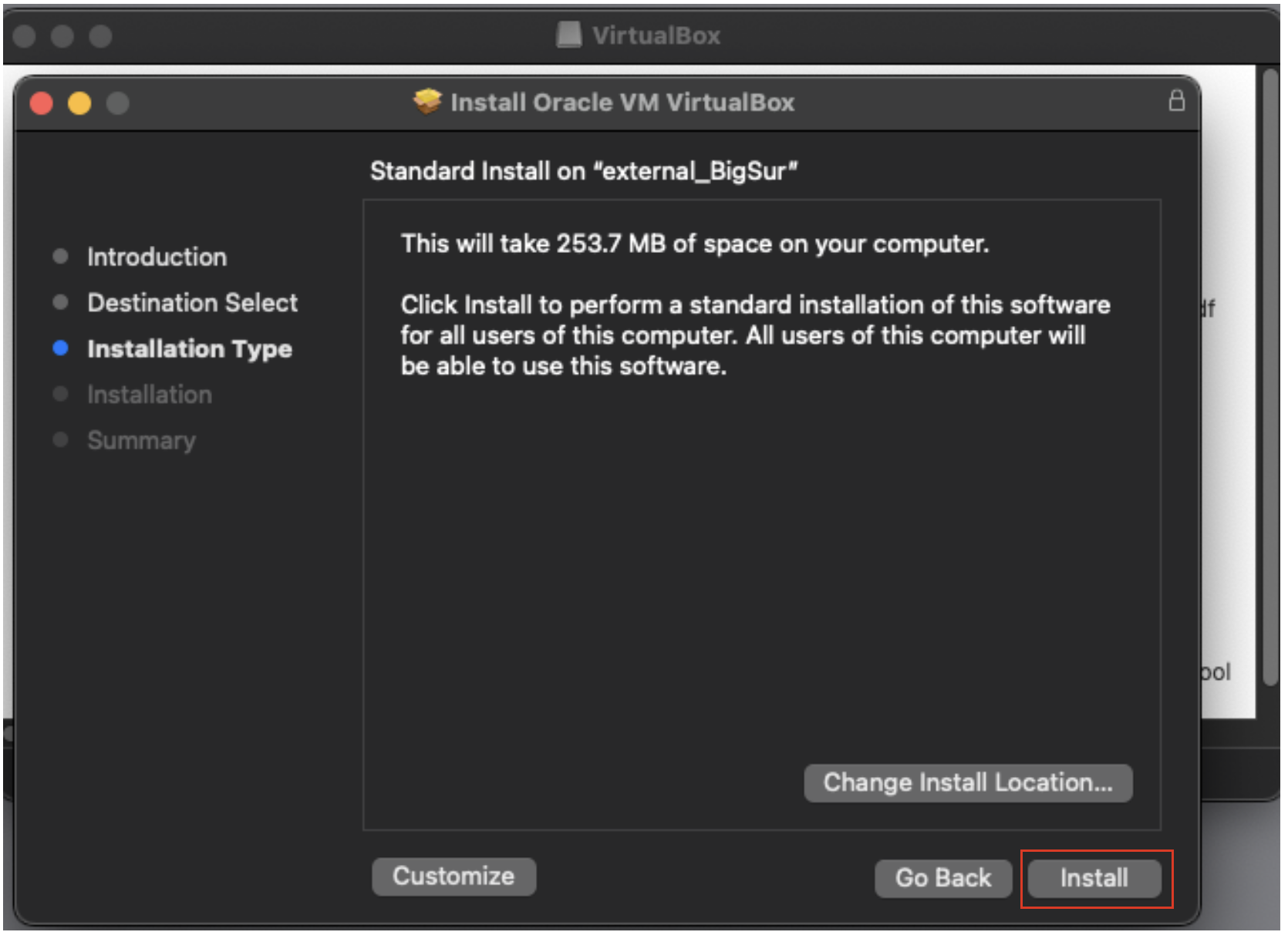
8. Authenticate using your login credentials to allow the installation.
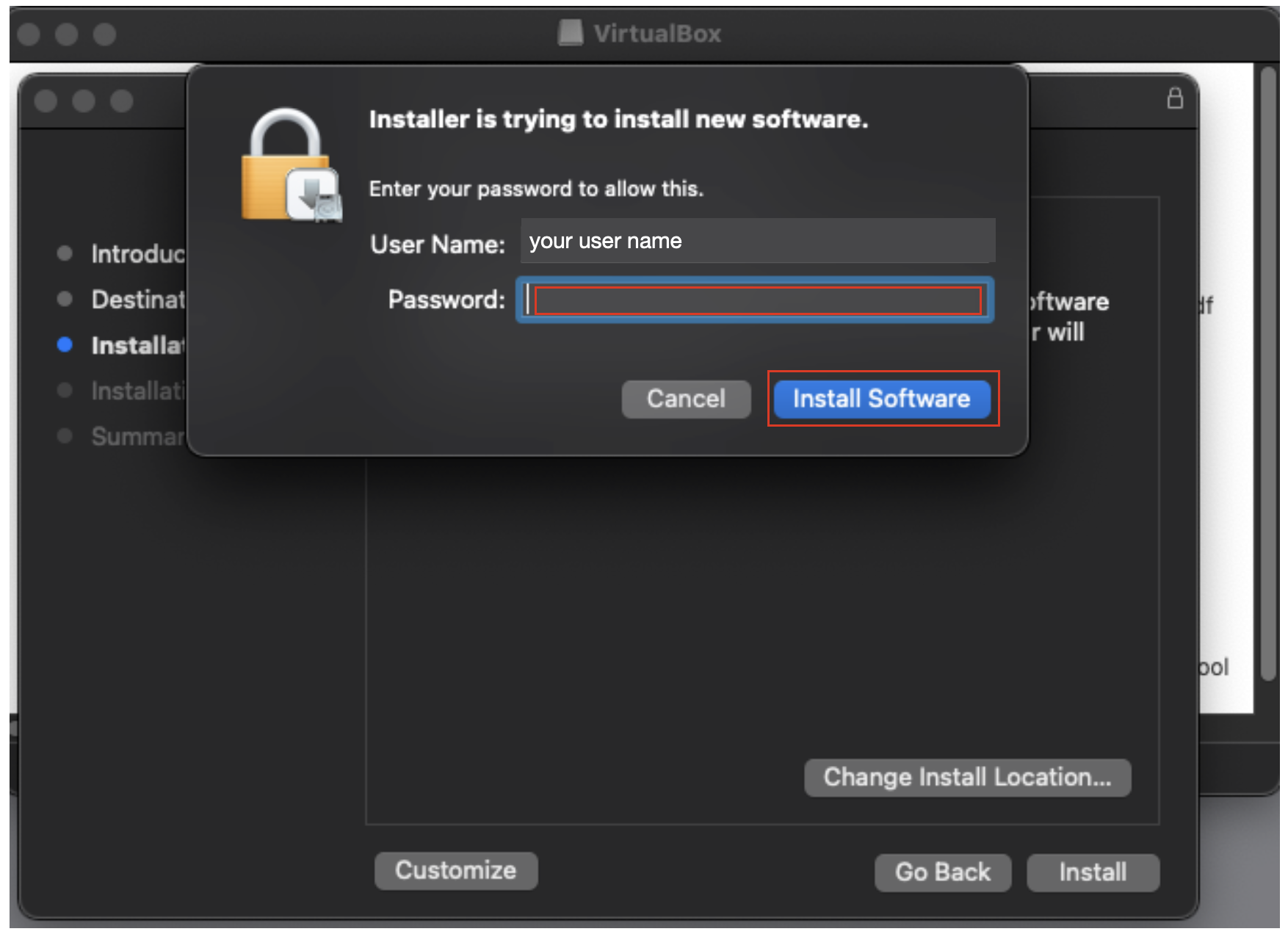
9. VirtualBox will issue a notification that the kernel extension it installed is currently blocked from running. Click OK.
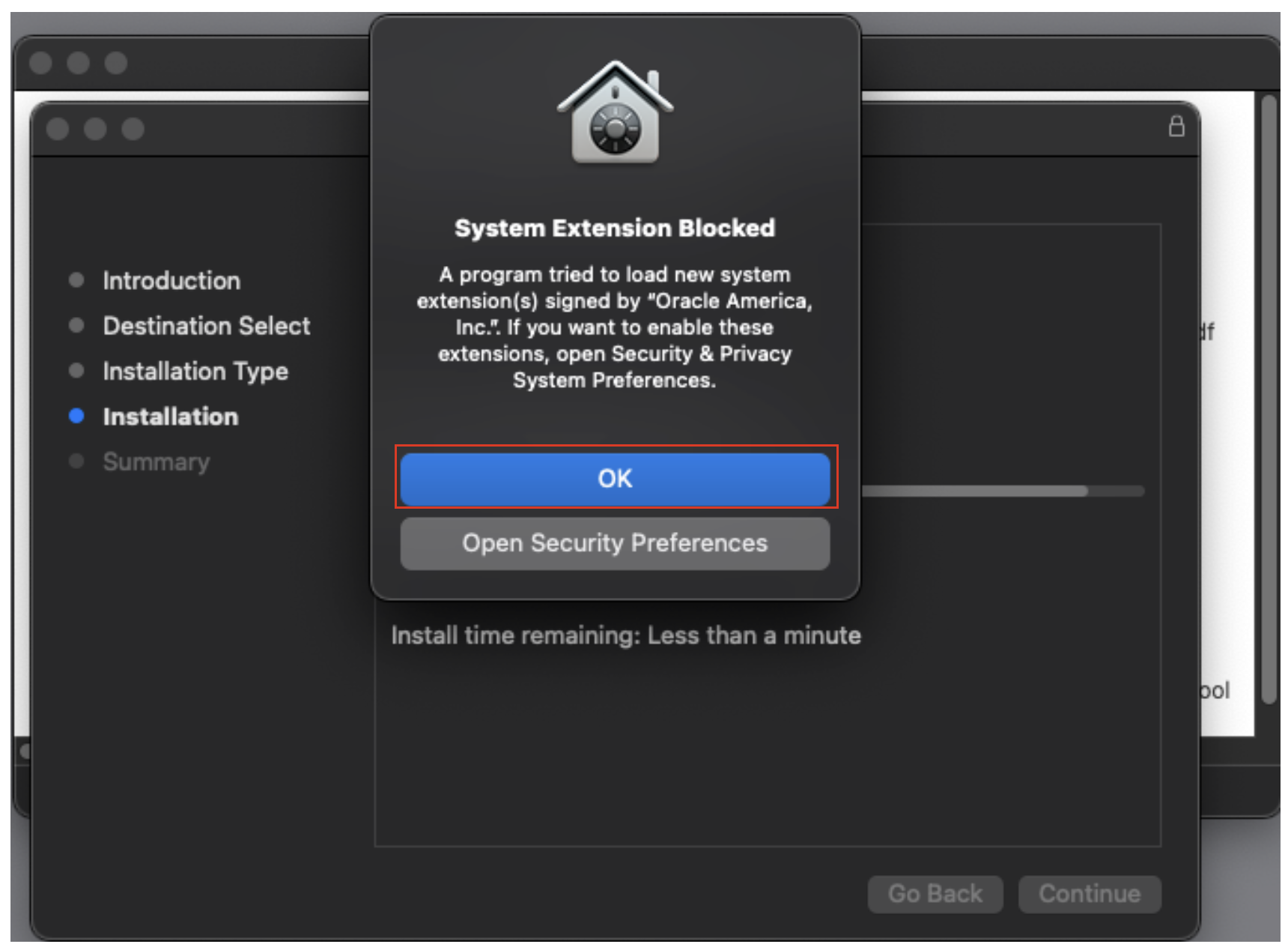
10. After the notification the install completed, go into the system security and privacy settings and authenticate with your login credentials.
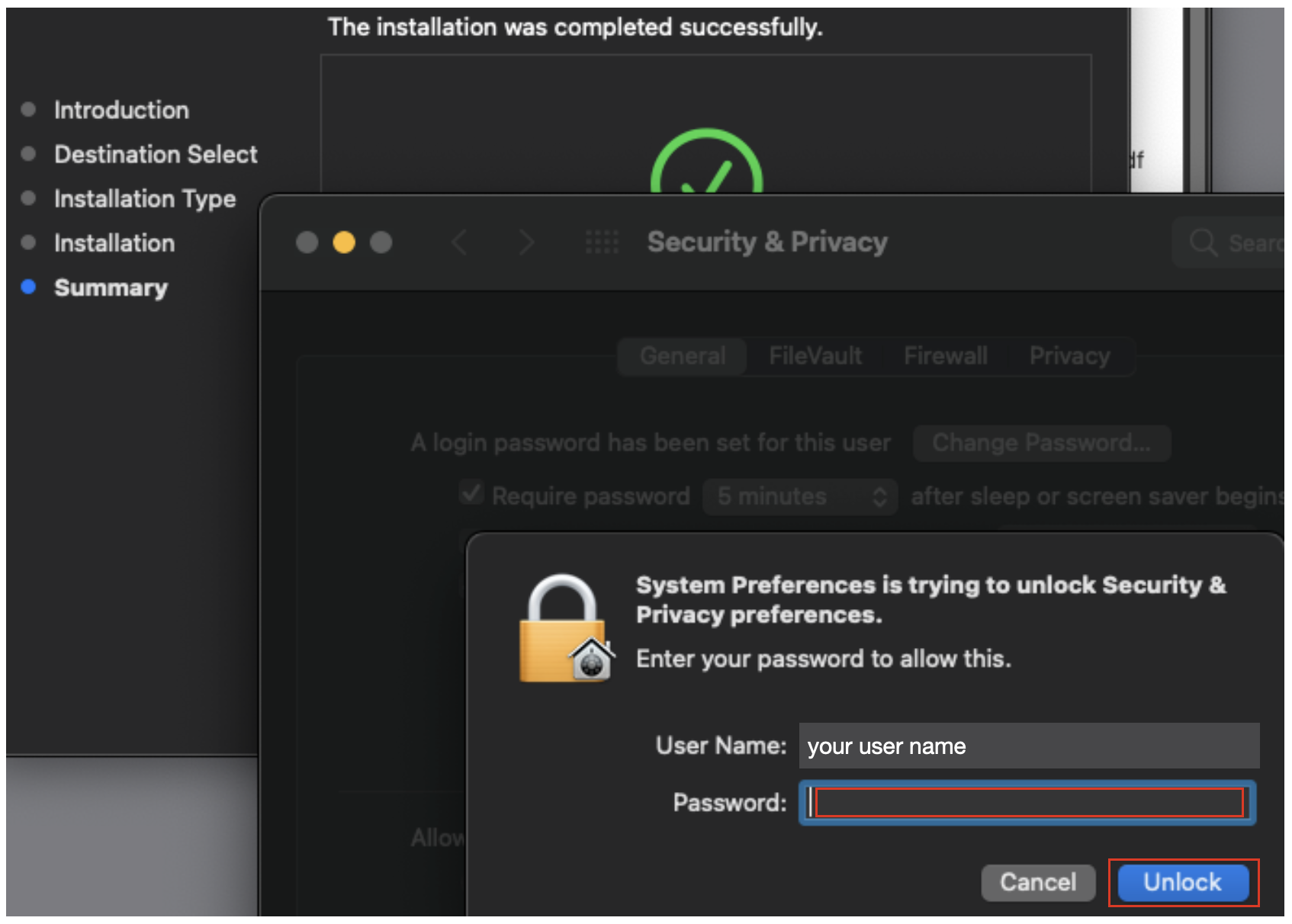
11. With the preferences unlocked, select allow to enable the VirtualBox extension to load.
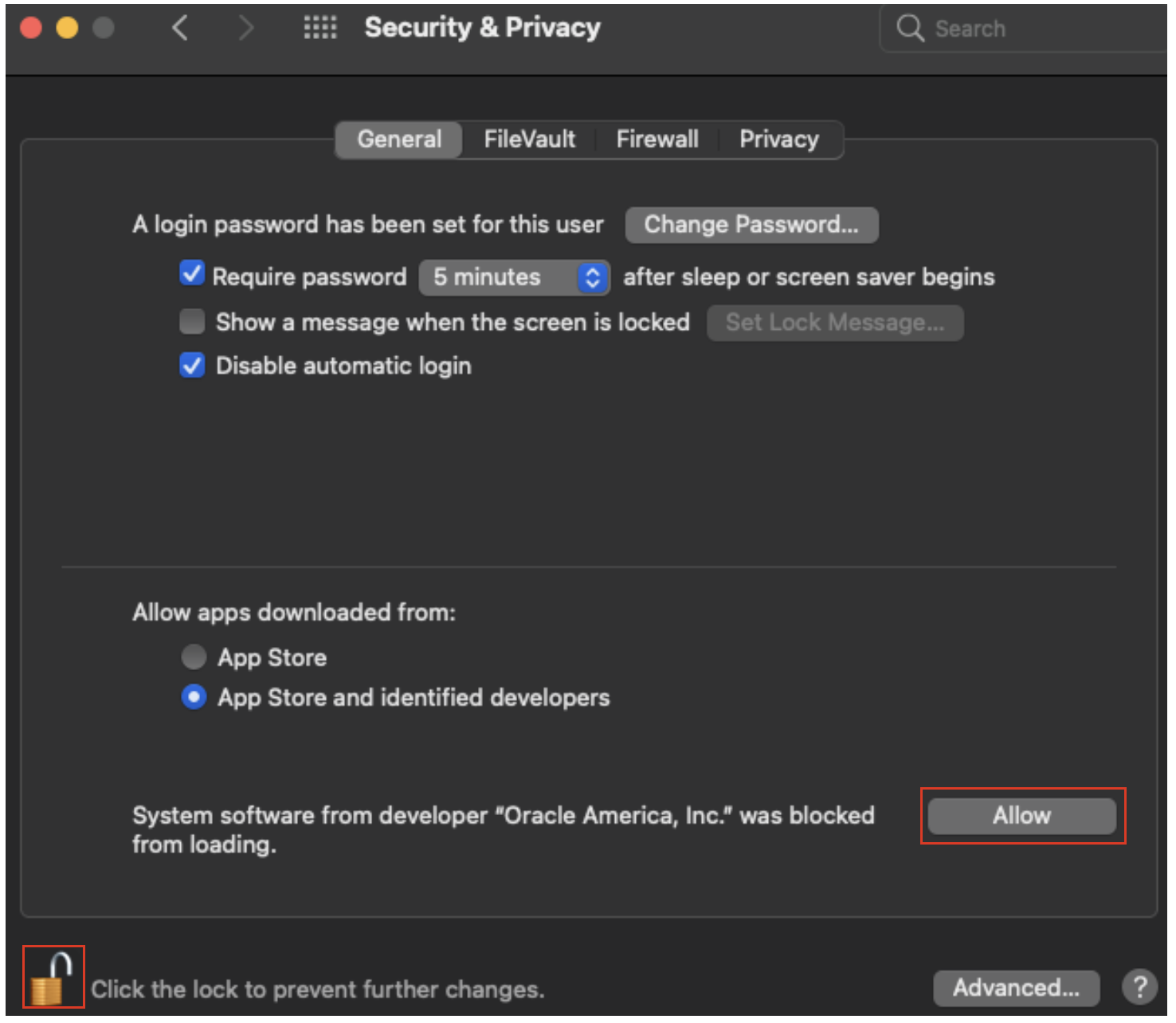
12. YOU SHOULD BE PROMPTED to restart the machine in order for the VirtualBox kernel extension to load and run. Select restart and after the reboot login to your account.
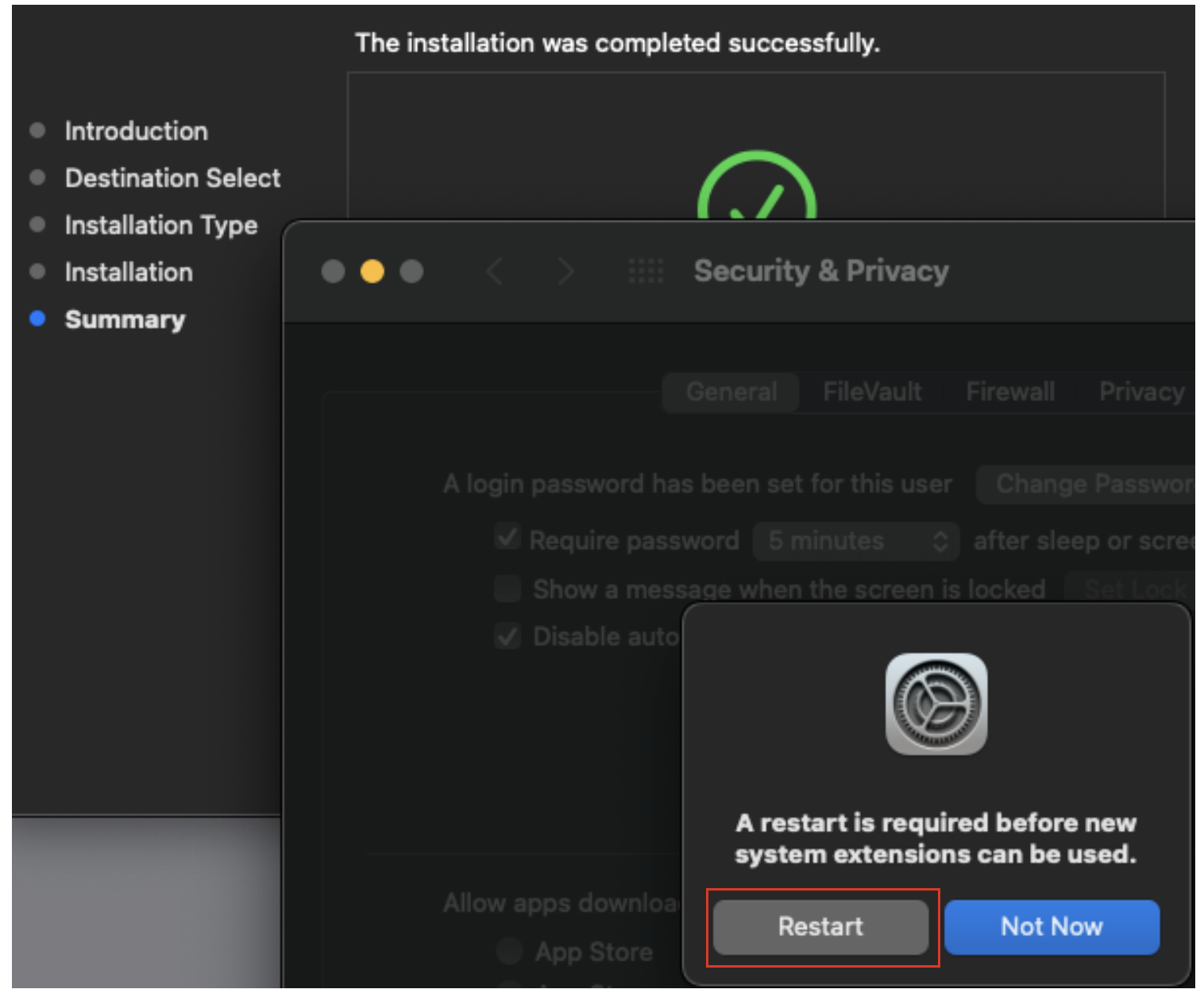
13. Check the VirtualBox application appears in the Applications folder.
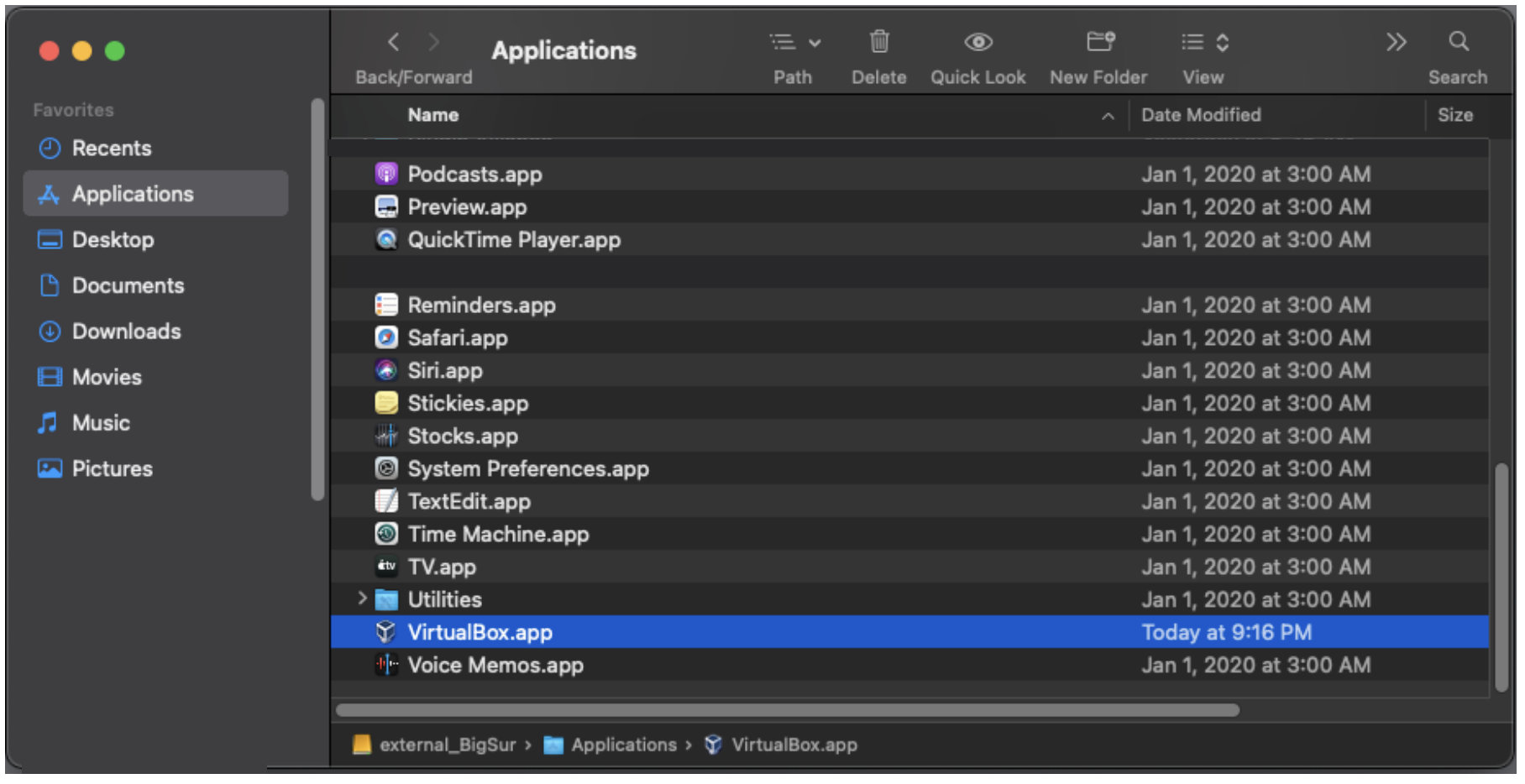
Retrieving Tutorial Data
1. At this point, the Ubuntu virtual machine should run including running the FreeView application from the terminal command line, e.g., display a volume (*.mgz file). Go back and review the previous documentation to setup and run the VM if this is not the case.
The tutorial data download archive needs ~8G of space and the uncompressed data needs ~14G of space. Find the location of the virtual machine folder on the host by right clicking on the entry for the virtual machine in the Virtual Box sidebar. On the Mac select “show in Finder” and on Windows select “show in Explorer”.
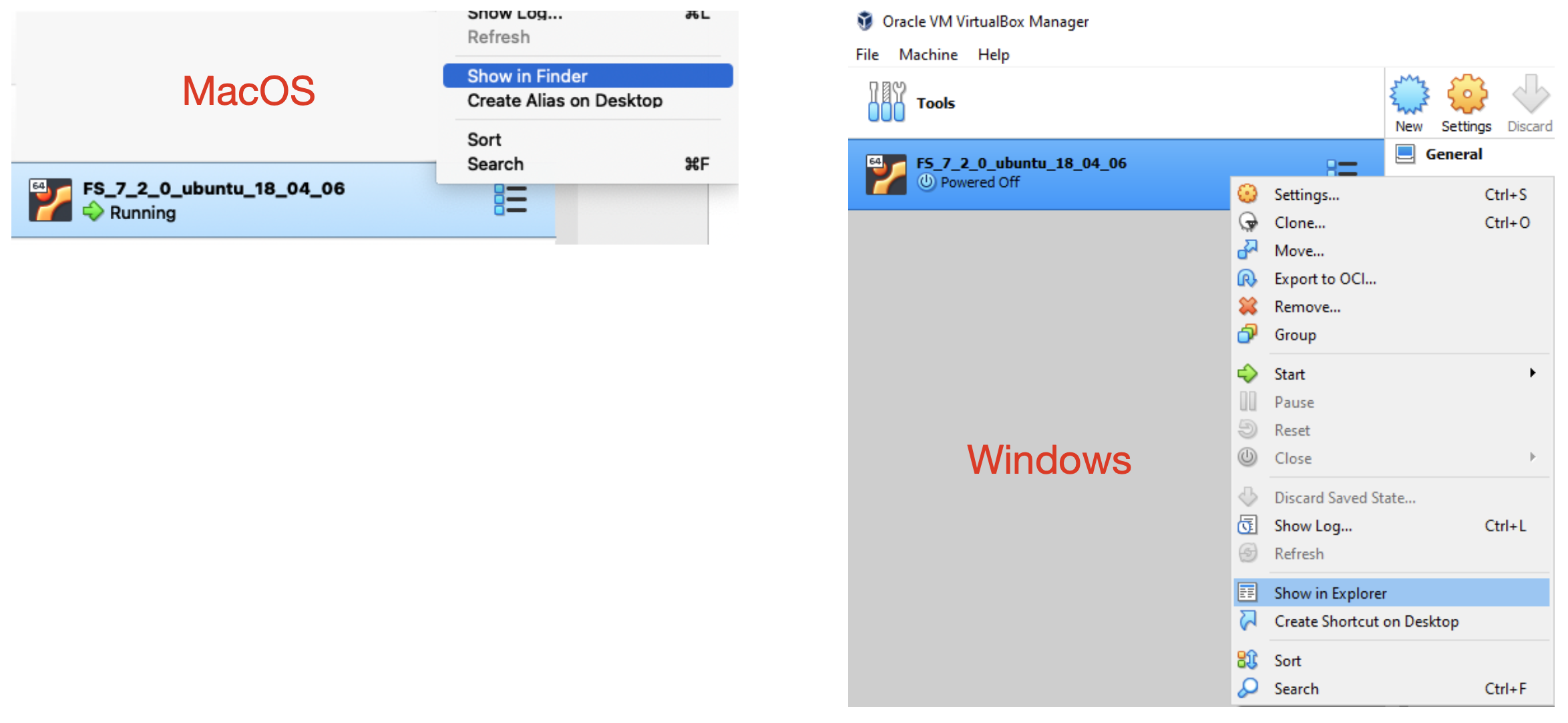
Check the disk where the VirtualBox folder resides has a least another ~25G of free space available. If that is not the case, then you will need to setup a new copy of the VM on a disk partition with more space. Alternately, you can clone your existing VM to another disk partition with more space. (See the VirtualBox documentation on how to clone a VM).
Space permitting, this would be a good time to make a snapshot of the VM. However, you may need an additional ~25G for the first VM snapshot, i.e., the partition would then need ~50G of free space. Do not create snapshots if there is not enough disk space. This is not necessary for the course, but should be done often if important work is being done in then VM and not being otherwise backed up.
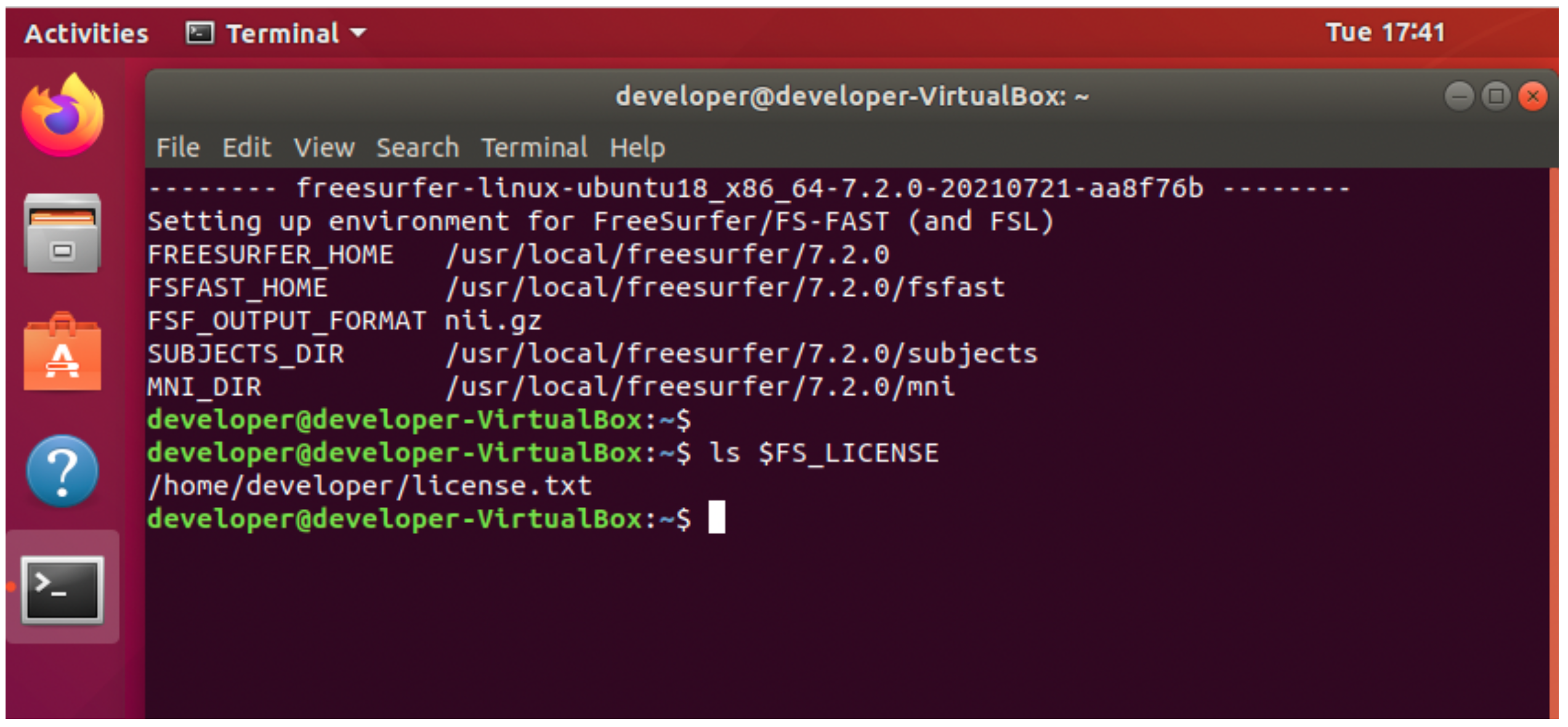
2. Open a new terminal window and check there are no reports of a missing license file. Per the instructions in the previous documents, the environment variable FS_LICENSE should point to your license file, e.g., license.txt.
3. Run the setup_tutorial_data command to download and setup the tutorial data for use with the FreeSurfer 7.2.0 release. The download may take 20-30 minutes depending upon your network connection. See the “eta” estimate to the right hand side of the progress bar for the “estimated time of arrival”.
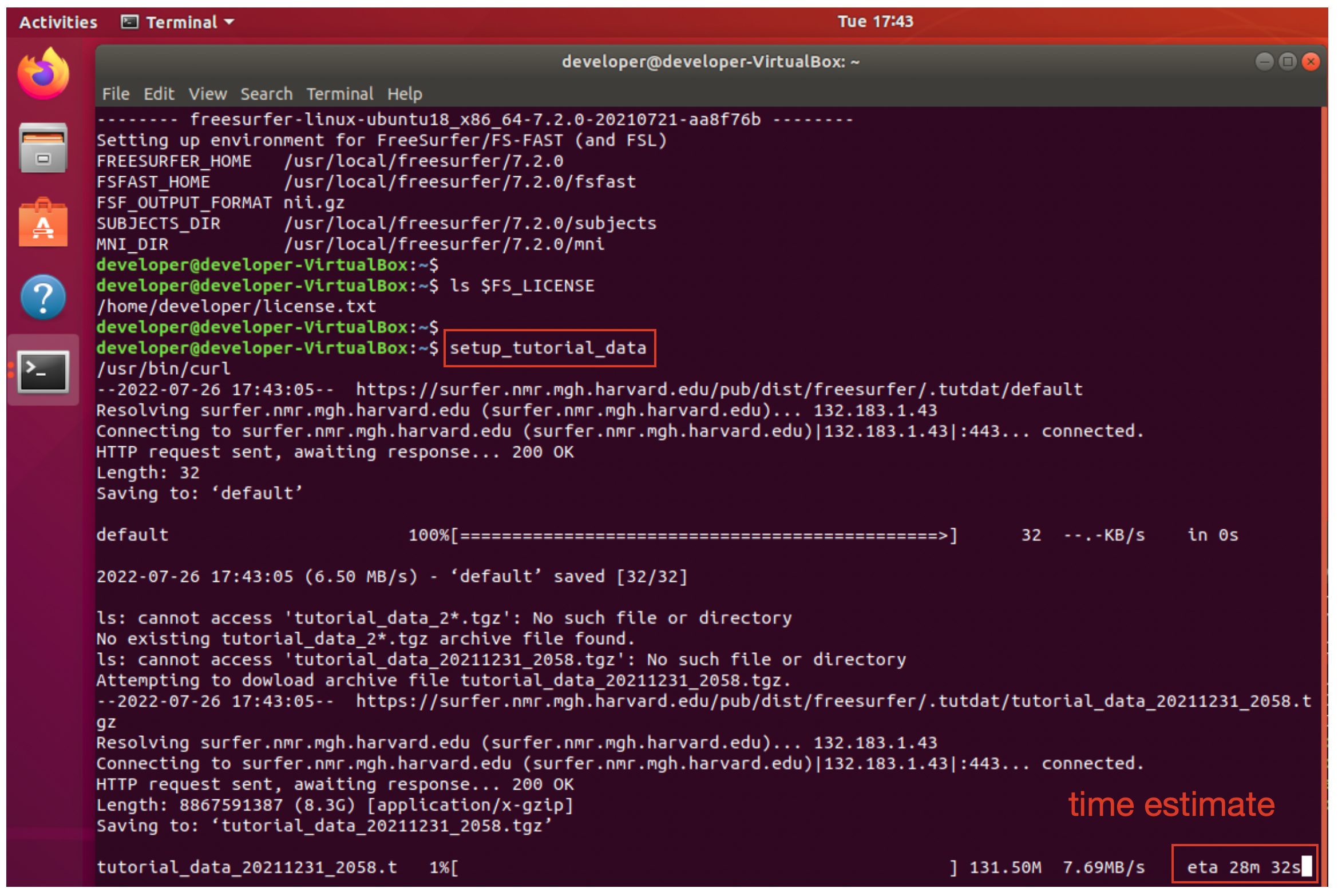
4. Example terminal output is shown below for the completed download of the tutorial data. Note the archive name, tutorial_data_20211231_2058, may be different if the data has changed.
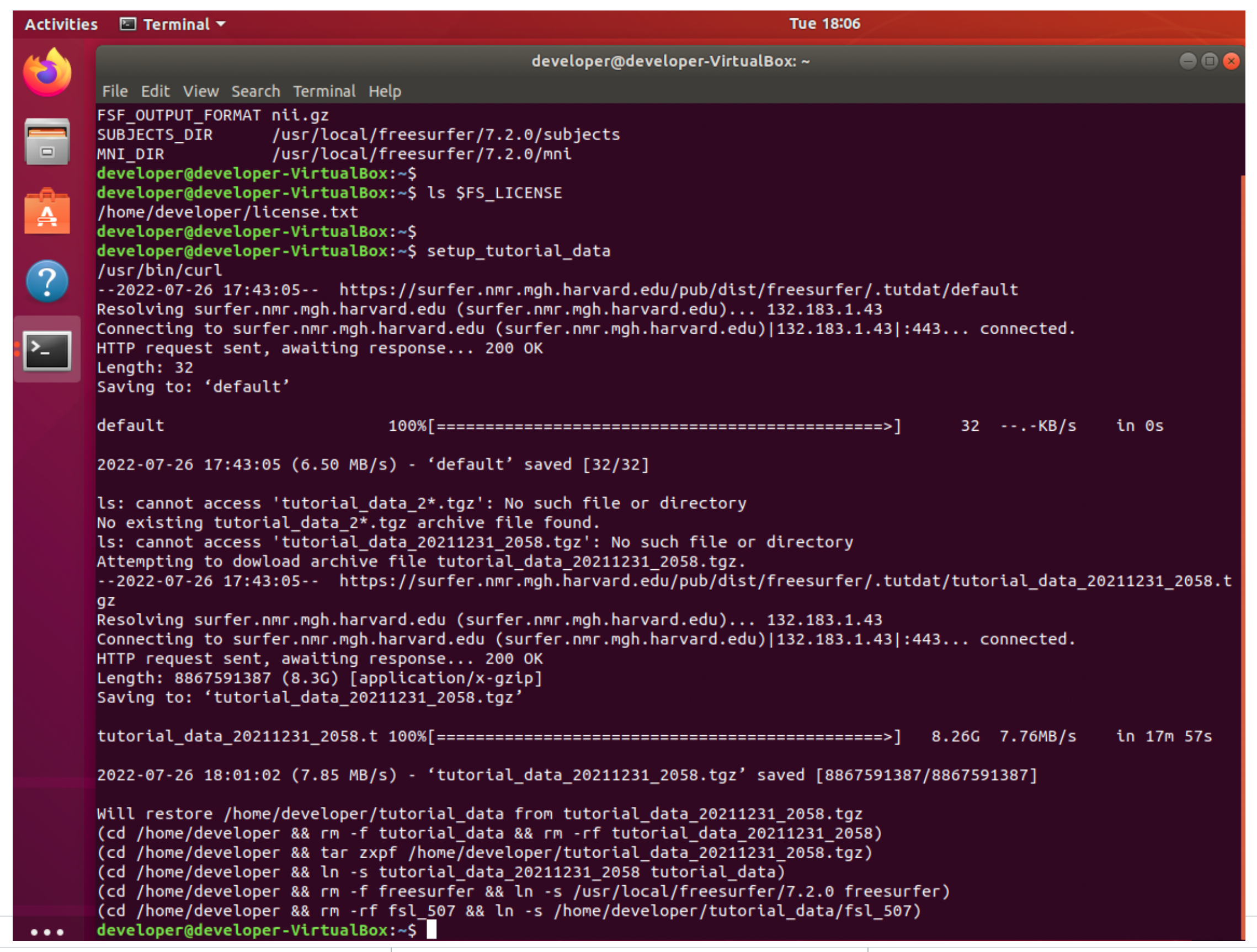
5. Close the current terminal window by clicking on the red X in the upper right hand corner of the toolbar.

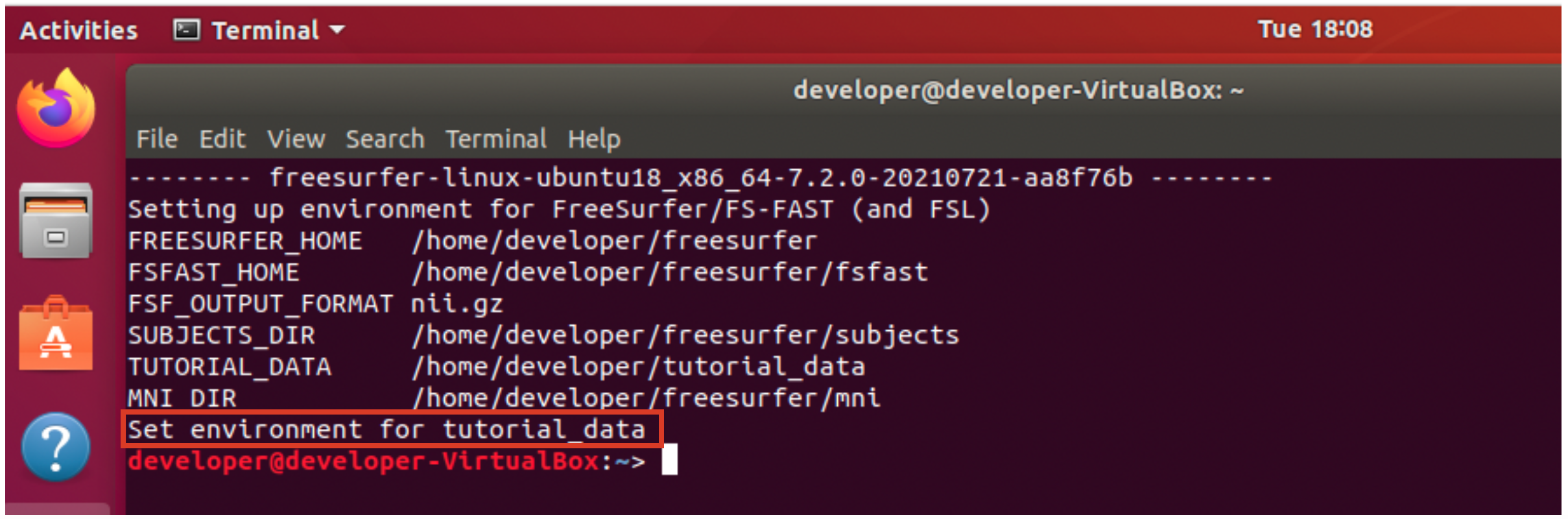
Open a new terminal window and check the last line of output is “Set environment for tutorial data”. Stop, do not proceed and check with the FreeSurfer team if this is not the case.
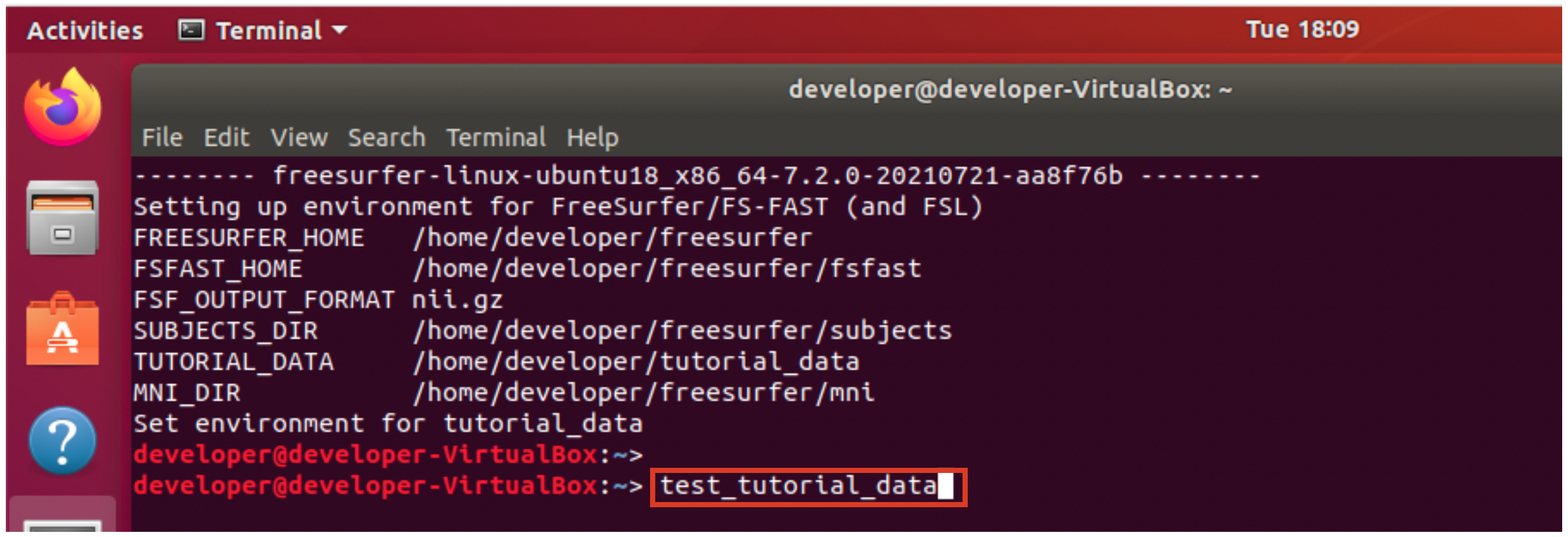
6. Run the test_tutorial_data command to test if your setup can run the tutorial commands. The test may take 20-30 minutes on a typical machine. You will see 80+ FreeView commands run and the FreeView GUI will automatically open and close. Do not manually close the FreeView window or interrupt the test.
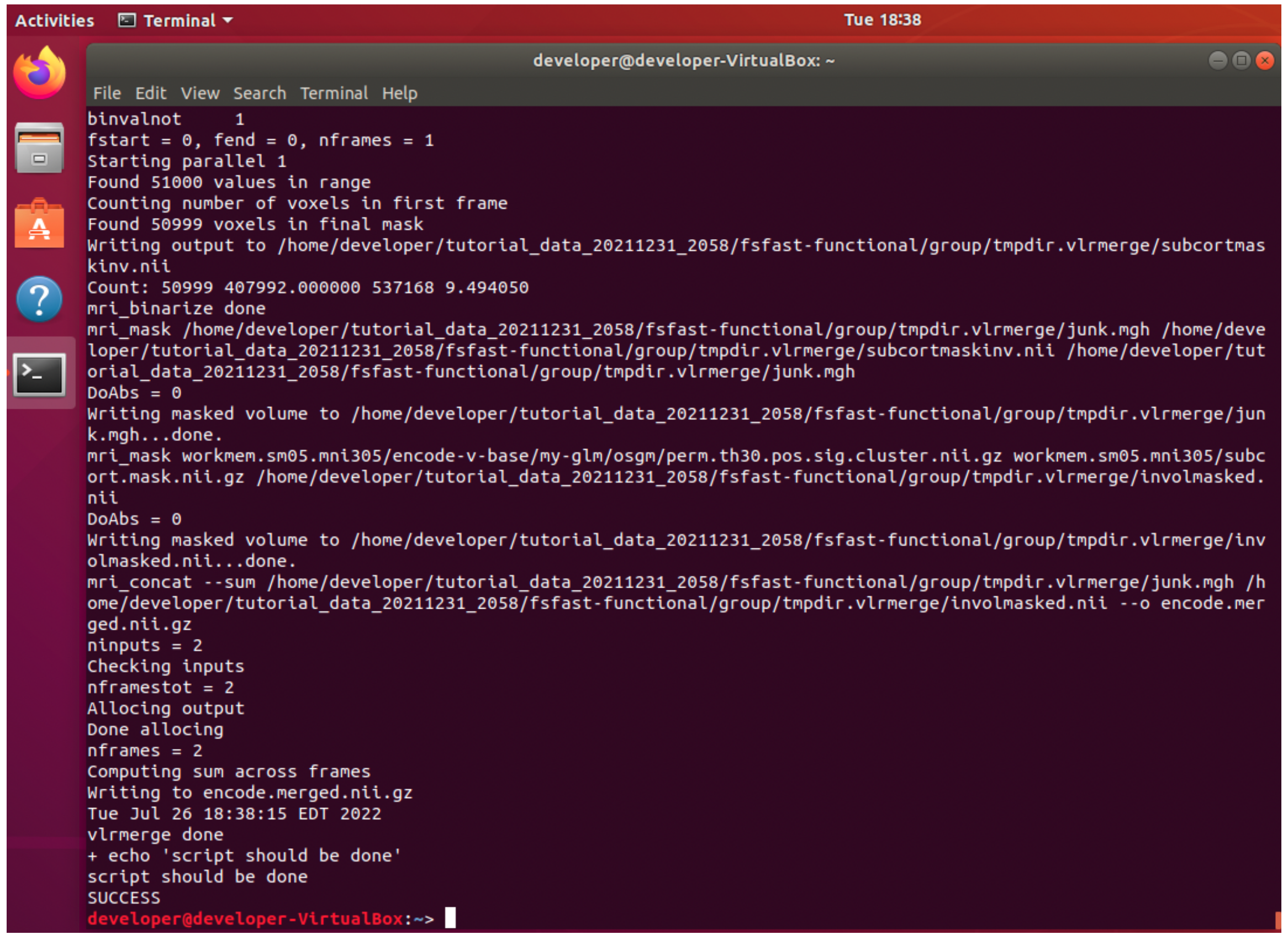
7. Example test output while running …
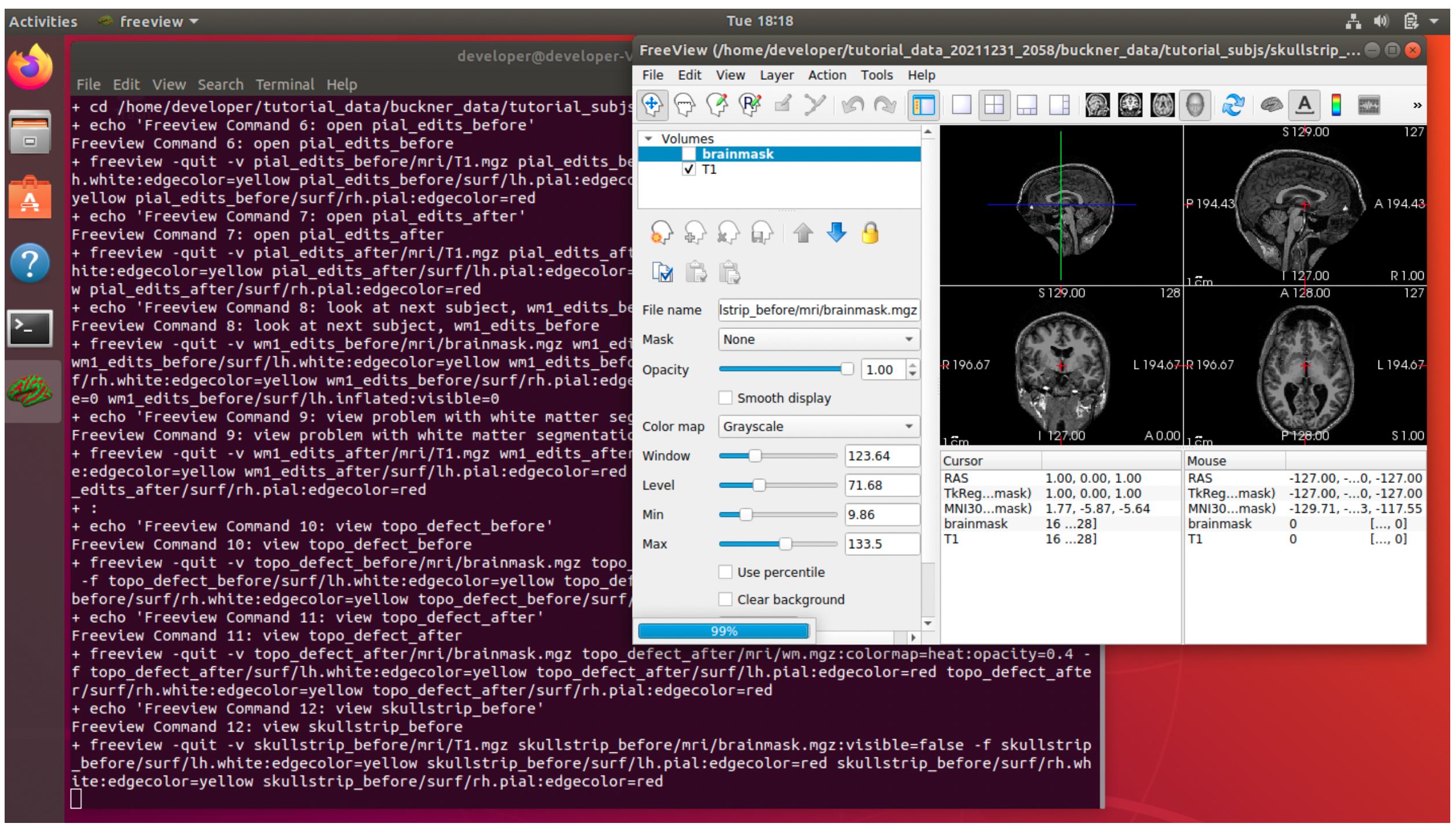
8. Check the test ends by displaying “SUCCESS” If you do not get this result, e.g., the test exits prematurely or exits with an error, then check with the FreeSurfer team. Successful output for the end of the test is shown below.
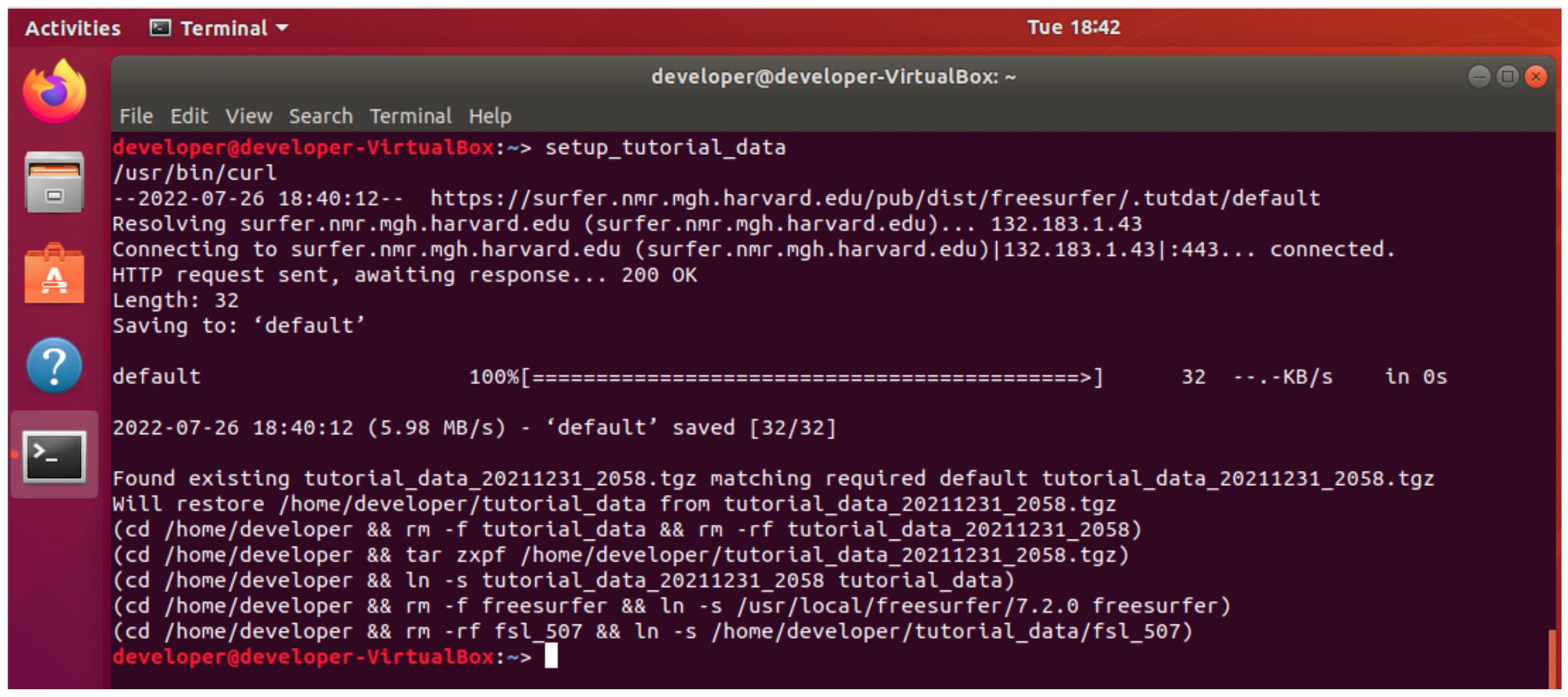
9. Lastly, run the setup_tutorial_data command again to reset the tutorial data to a clean state. The previously downloaded tutorial data will be used unless the tutorial data has changed since the last download. When the command finishes you should be able to run the tutorial commands from scratch. Run this command to reset the data before day 1 of the FreeSurfer course. Make sure any new terminal window reports “Set environment for tutorial data”.
You are now prepared for the course! There are other tutorials here (link pending) if you wish to try out your system before the course or if you wish to go over more material, but this is optional.
