|
Size: 3643
Comment:
|
Size: 8419
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 16: | Line 16: |
| The main options are: | |
| Line 19: | Line 20: |
| ||--hemisphere ||Must be left, right, or both || ||--slice_thickness ||Slice thickness in mm (if unsure, give conservative estimate, i.e., a bit lower value). || ||--photo_resolution ||Resolution of the photos in mm (if using PhotoToools this would be 0.1). || |
|
| Line 27: | Line 34: |
| ||--slice_thickness ||Slice thickness in mm. || ||--photo_resolution ||Resolution of the photos in mm. || |
|
| Line 30: | Line 37: |
-h, --help show help message --input_photo_dir [INPUT_PHOTO_DIR] Directory with input photos (required) --input_segmentation_dir [INPUT_SEGMENTATION_DIR] Directory with input slab masks / segmentations (required) --hemisphere HEMISPHERE hemisphere; must be left, right, or both (required) --slice_thickness SLICE_THICKNESS Slice thickness in mm (required); will be finetuned if possible --photo_resolution PHOTO_RESOLUTION Resolution of the photos in mm (required) --output_directory OUTPUT_DIRECTORY Output directory with reconstructed photo volume and reference (required) --ref_mri REF_MRI Reference MRI scan (if available) --ref_mri_synthseg REF_MRI_SYNTHSEG SynthSeg of reference MRI scan (will be computed if it does not exist) --ref_mri_synthsr REF_MRI_SYNTHSR SynthSR of reference MRI; only needed if MRI is not 1mm T1 (will be computed if it does not exist) --low_field_synthsr Use low-field version of SynthSR (eg for Hyperfine scans) --input_roi_dir INPUT_ROI_DIR Directory with ROi masks to deform to photo reconstruction (optional) --ref_mesh REF_MESH Reference surface mesh (if available) --mesh_reorient_with_indices MESH_REORIENT_WITH_INDICES Indices to reorient mesh (see PhotoTools page in FreeSurfer wiki) --fresh_tissue Uses more lenient regularizers to accommodate fresh tissue --photos_of_posterior_side Use when photos are taken of posterior side of slabs (default is anterior side) --order_posterior_to_anterior Use when photos are ordered from posterior to anterior (default is anterior to posterior) --initial_stretch_factor_lr INITIAL_STRETCH_FACTOR_LR Initialize stretch of photos in left-right direction by this factor (useful with squashed brains) --weights WEIGHTS CSV file with slab weights (follows order of photos). Format is just: weight1,weight2,...,weightN --thickness_cap MAX when using weights, limit the maximum estimated thickness to this value (in mm). This is useful when the geometric estimation of thicknesses is wrong. The code (without this option) tries to detect these situations automatically and tells you when to enable this option --equalize_images Use to equalize images (useful if they have low contrast, but can hurt the machine learning imputation) --skip_bfgs Use to skip BFGS finetuning (i.e., do only Adam) --threads THREADS Number of cores to be used. Default is 1. You can use -1 to use all available cores --gpu GPU Index of GPU to use (default is None, i.e., CPU mode) --deform_recon_dir DEFORM_RECON_DIR Directory with FS dir of reference, to deform surfaces etc (expects to find deform_recon_dir/surf) (optional) --cp_spacing_2d CP_SPACING_2D (Advanced) Control point spacing for 2D deformation --cp_spacing_3d CP_SPACING_3D (Advanced) Control point spacing for 3D deformation --k_lncc_mri K_LNCC_MRI (Advanced) Weight of LNCC between reference MRI and reconstruction --k_dice_mri K_DICE_MRI (Advanced) Weight of Dice between masks of reference and reconstruction --k_dif_slice_loss K_DIF_SLICE_LOSS (Advanced) Weight of SSD between consecutive slices of reconstruction --k_mesh_loss K_MESH_LOSS (Advanced) Weight of absolute distance to edge of masks from mesh vertices --k_regularizer K_REGULARIZER (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of log_det(affine matrices) --k_regularizer_nonlin K_REGULARIZER_NONLIN (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of 2D nonlinear deformation of photos --k_regularizer_nonlin3d K_REGULARIZER_NONLIN3D (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of 3D nonlinear deformatin of reference |
Co-registration of dissection photographs of coronal slabs into a 3D volume
For FreeSurfer 8.0 or development versions downloaded before May 2025, please see https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/mri_3d_photo_recon_2024.
If you use this tools in your analysis, please cite:
* Machine learning of dissection photographs and surface scanning for quantitative 3D neuropathology. H Gazula, H Tregidgo, B Billot, Y Balbastre, J Williams Ramirez, R Herisse, LJ Deden-Binder, A Casamitjana, EJ Melief, CS Latimer, MD Kilgore, M Montine, E Robinson, E Blackburn, MS Marshall, TR Connors, DH Oakley, MP Frosh, SI Young, K Van Leemput, AV Dalca, B Fischl, CL Mac Donald, CD Keene, B Hyman, and JE Iglesias. Under revision.)
This is a newer version of our older tool with several key improvements:
- More flexible framework, accepting a variable number of references (e.g., surface scan and/or MRI scan or MNI atlas etc).
- Faster optimization
- Easier configuration of parameters: it self configures depending on type(s) of input(s)
- Supports slabs of variable thickness
- New feature: machine learning interpolation to 1mm slab thickness (fun stuff! See pictures below)
The main options are: mri_3d_photo_recon -h
--input_photo_dir |
Directory with input pixel-corrected photos. |
--input_segmentation_dir |
Directory with input slab masks/segmentations |
--hemisphere |
Must be left, right, or both |
--slice_thickness |
Slice thickness in mm (if unsure, give conservative estimate, i.e., a bit lower value). |
--photo_resolution |
Resolution of the photos in mm (if using PhotoToools this would be 0.1). |
--ref_mask |
When using a binary volume as a reference. |
--ref_surface |
Using a 3D surface scan as a reference. |
--ref_soft_mask |
Using the provided average atlas. Best for using retrospective processing on data without a better reference. |
--mesh_reorient_with_indices |
Vertex indices of the frontal pole, occipital pole, and top of the central sulcus, separated with commas, for mesh alignment. |
--photos_of_posterior_side |
Use when photos are taken of the posterior side of slabs (default is anterior side). |
--order_posterior_to_anterior |
Use when photos are ordered from posterior to anterior (default is anterior to posterior). |
--allow_z_stretch |
Use to adjust the slice thickness to best match the reference. You should probably *never* use this with soft references (ref_soft_mask). |
--rigid_only_for_photos |
Switch on if you want photos to deform only rigidly (not affine). |
||--output_directory ||Output directory with reconstructed photo volume and reference ||
- -h, --help show help message --input_photo_dir [INPUT_PHOTO_DIR]
- Directory with input photos (required)
- Directory with input slab masks / segmentations (required)
- hemisphere; must be left, right, or both (required)
- Slice thickness in mm (required); will be finetuned if possible
- Resolution of the photos in mm (required)
- Output directory with reconstructed photo volume and reference (required)
- Reference MRI scan (if available)
SynthSeg of reference MRI scan (will be computed if it does not exist)
- SynthSR of reference MRI; only needed if MRI is not 1mm T1 (will be computed if it does not exist)
- Use low-field version of SynthSR (eg for Hyperfine scans)
- Directory with ROi masks to deform to photo reconstruction (optional)
- Reference surface mesh (if available)
Indices to reorient mesh (see PhotoTools page in FreeSurfer wiki)
- Uses more lenient regularizers to accommodate fresh tissue
- Use when photos are taken of posterior side of slabs (default is anterior side)
- Use when photos are ordered from posterior to anterior (default is anterior to posterior)
- Initialize stretch of photos in left-right direction by this factor (useful with squashed brains)
- CSV file with slab weights (follows order of photos). Format is just: weight1,weight2,...,weightN
- when using weights, limit the maximum estimated thickness to this value (in mm). This is useful when the geometric estimation of thicknesses is wrong. The code (without this option) tries to detect these situations automatically and tells you when to enable this option
- Use to equalize images (useful if they have low contrast, but can hurt the machine learning imputation)
- Use to skip BFGS finetuning (i.e., do only Adam)
- Number of cores to be used. Default is 1. You can use -1 to use all available cores
- Index of GPU to use (default is None, i.e., CPU mode)
- Directory with FS dir of reference, to deform surfaces etc (expects to find deform_recon_dir/surf) (optional)
- (Advanced) Control point spacing for 2D deformation
- (Advanced) Control point spacing for 3D deformation
- (Advanced) Weight of LNCC between reference MRI and reconstruction
- (Advanced) Weight of Dice between masks of reference and reconstruction
- (Advanced) Weight of SSD between consecutive slices of reconstruction
- (Advanced) Weight of absolute distance to edge of masks from mesh vertices
- (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of log_det(affine matrices)
- (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of 2D nonlinear deformation of photos
- (Advanced) Weight of regularizer of 3D nonlinear deformatin of reference
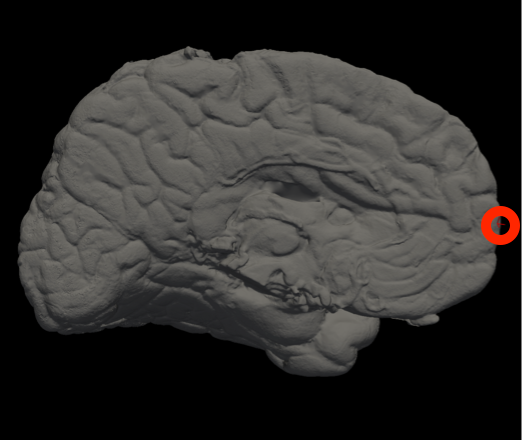
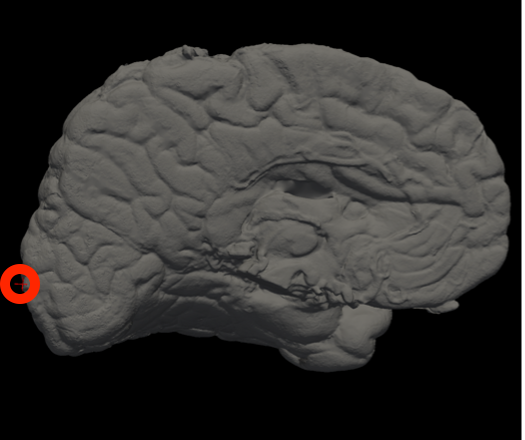
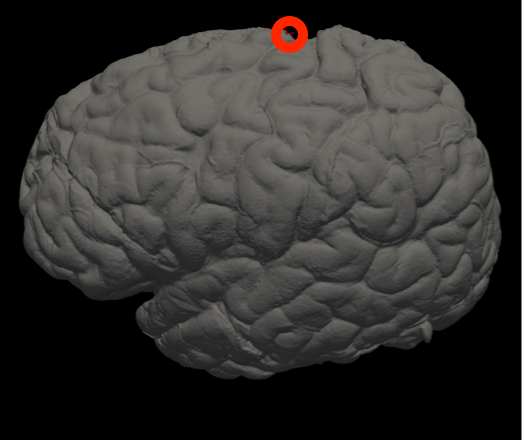
In Freeview, you can find the number corresponding to the vertices of each anatomical area to use in the --mesh_reorient_with_indices flag. These indices should be comma-separated in the order: frontal pole, occipital pole, and top of the central sulcus.
|
|
|
Frontal Pole |
Occipital Pole |
Top of the central sulcus |
For example, the --mesh_reorient_with_indices flag might look like this:
- –mesh_reorient_with_indices 999999,999999,999999
Example for running reconstruction
- mri_3d_photo_recon \
- --input_photo_dir ./deformed \
- --input_segmentation_dir ./connected_components \
- --ref_surface ./mesh/case.stl \
- --mesh_reorient_with_indices 999,1010,333333 \
- --photos_of_posterior_side --allow_z_stretch \
- --slice_thickness 8 \
- --photo_resolution 0.1