| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 77: | Line 77: |
| After the bad skull strip has been improved, you can run the following command to regenerate Freesurfer output based on the new brainmask.mgz | After the bad skull strip has been improved, you can run the following command to regenerate Freesurfer output based on the new brainmask.mgz. |
Fixing a bad skull strip
To follow this exercise exactly be sure you've downloaded the tutorial data set before you begin. If you choose not to download the data set you can follow these instructions on your own data, but you will have to substitute your own specific paths and subject names.
Occasionally, the skull stripping step either removes more than just the skull, causing part of the brain to be removed as well, or too little, leaving behind portions of the skull. Both of these problems need to be corrected before continuing to the next step, either by manually editing the volumes or by adjusting input parameters to the skull stripping step, and running the skull strip again until a good result is obtained. Often the sagittal view reveals skull strip failures. Note that the inflated 3D surface is a less reliable gauge of skull strip failure unless large portions of the brain are missing, or lots of skull is retained.
skullstrip1_before has a poor skull strip, an entire hemisphere of the cerebellum has been stripped away along with the skull. This page will walk you through the process of fixing this particular subject and also offer suggestions for fixing other common skull stripping problems.
freeview -v skullstrip1_before/mri/T1.mgz \ skullstrip1_before/mri/brainmask.mgz \ -f skullstrip1_before/surf/lh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ skullstrip1_before/surf/lh.pial:edgecolor=red \ skullstrip1_before/surf/rh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ skullstrip1_before/surf/rh.pial:edgecolor=red
If you look at coronal slice 91 for skullstrip1_before you can see that the brainmask.mgz volume (the first picture) is missing the right hemisphere of the cerebellum and that it is present in the T1.mgz volume (the second picture). Note that Freesurfer displays slices in radiological view so the right hemisphere cerebellum skull strip issue is seen here on the left side:
In general there are two ways to fix a volume when there is something missing from the cortex or cerebellum, you can clone the missing pieces in manually or you can adjust the parameters of mri_watershed to do it automatically. For this case, because there is such a lot missing on so many slices you should adjust the parameters of mri_watershed.
Adjusting watershed parameters
The watershed algorithm is used during the skull stripping step to find a boundary between the brain and skull. The mri_watershed program uses a default preflooding height of 25 percent. If we want the algorithm to be more conservative (i.e. if part of the brain has been removed), you will want to make that number larger than 25. If you want the algorithm to be more aggressive (i.e. part of the skull has been left behind), you will want to make the height less than 25. There aren't any hard and fast rules about how to select your height value. You can adjust the preflooding height by passing the following flag to recon-all:
recon-all -skullstrip -wsthresh <h> -clean-bm -subjid <subject name>
where <h> is replaced with the preflooding height you'd like to use and <subject name> is replaced with your subject. The clean-bm flag is used to instruct recon-all to write over the old brainmask.mgz volume with your new edits. If you do not use this flag your changes will not take effect.
Part of the brain is missing
Now we will take another look at the first volume we looked at, where part of the cerebellum had been removed. If you suspect that certain anatomy could be an outlier, and may be responsible for making the skullstripping step fail or produce poor results then you can try using the -no-wsgcaatlas flag (wsgcaatlas = with skull gaussian classifier array atlas). You can adjust the watershed threshold by passing the -wsthresh flag to recon-all. In this instance, since too much was removed, we want to raise the watershed threshold so use the command:
recon-all -skullstrip -wsthresh 35 -clean-bm -no-wsgcaatlas -subjid skullstrip1_before
Take a look at your output volume (brainmask.mgz has been changed) along with the original T1 volume (T1.mgz), and verify the result of the new skull stripping is correct.
freeview -v skullstrip1_after/mri/T1.mgz \ skullstrip1_after/mri/brainmask.mgz \ -f skullstrip1_after/surf/lh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ skullstrip1_after/surf/lh.pial:edgecolor=red \ skullstrip1_after/surf/rh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ skullstrip1_after/surf/rh.pial:edgecolor=red
Using gcut
When the skull stripping has left a small part of dura left, it is quicker to try and rerun the skullstrip step using the -gcut flag than to do manual editing. This flag removes any extra dura that could influence the surfaces.
recon-all -skullstrip -clean-bm -gcut -subjid <subject name>
INFO: Care must be taken to thoroughly inspect your data when using -gcut. In particular, inpsect the edges of gm and cerebellum for over-aggressive cutting. Open the brainmask.gcuts.mgz volume in freeview to view the voxels which gcut has removed. We recommend viewing the brainmask.gcuts.mgz overlayed on the T1.mgz to clearly see which voxels have been removed by gcut.
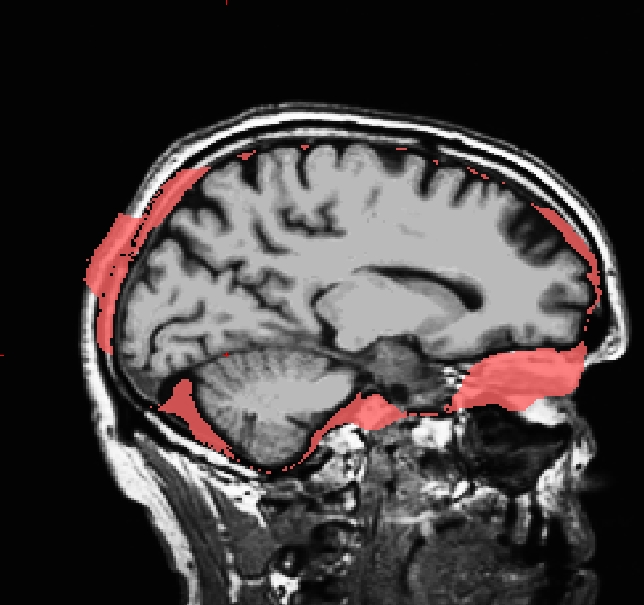
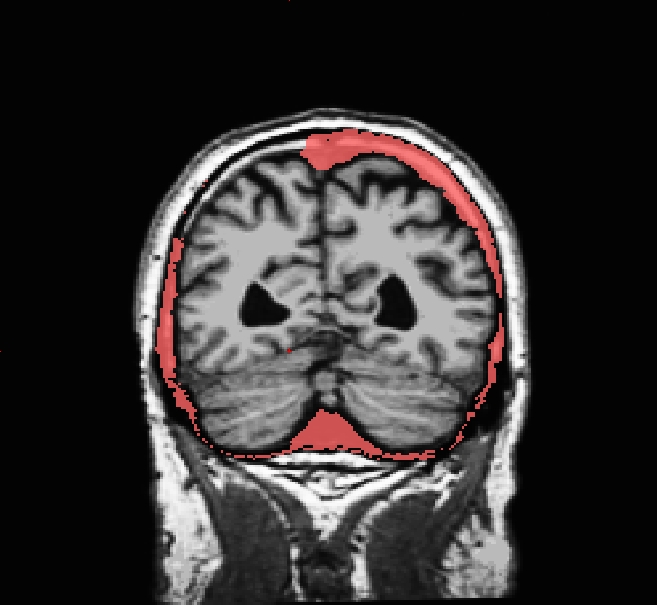
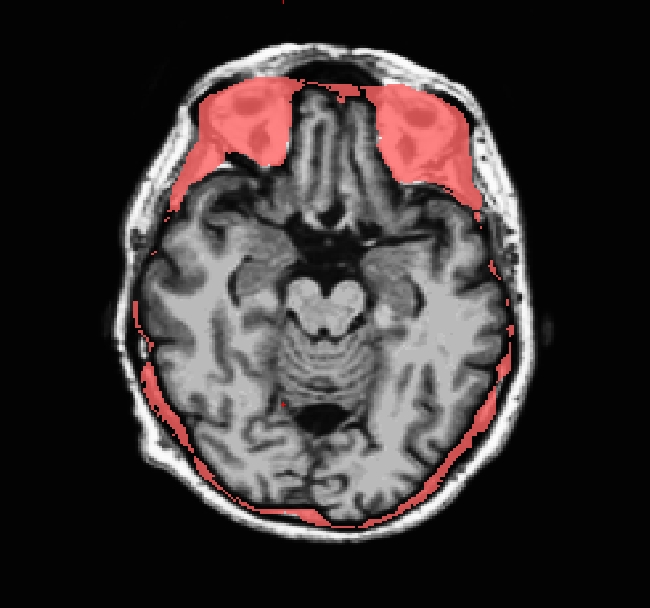
Use talairach_with_skull_2.lta
During the skull-strip stage, the registration file talairach_with_skull.lta is created by mri_em_register in order to make use of the atlas to find skull. But in the autorecon2 stage, the registration file talairach_with_skull_2.lta is created, and this one is created with the benefit of the mri_ca_register stage, and so tends to be a tiny bit more accurate than talairach_with_skull.lta, and so it is possible that the skull-strip will work better with this registration file. So to make use of it:
cd $SUBJECTS_DIR/yoursubj/mri/transforms cp talairach_with_skull.lta bak cp talairach_with_skull_2.lta talairach_with_skull.lta recon-all -s yoursubj -skullstrip -clean-bm -clean-lta
Inspect the brainmask.mgz after this completes.
Regenerating surfaces after the bad skull strip is fixed
After the bad skull strip has been improved, you can run the following command to regenerate Freesurfer output based on the new brainmask.mgz.
recon-all -autorecon-pial -subjid <subject name>
Do not run this command if you are conducting the tutorial!
