SynthStrip: Skull-Stripping for Any Brain Image
Andrew Hoopes, Jocelyn S. Mora, Adrian V. Dalca, Bruce Fischl, Malte Hoffmann
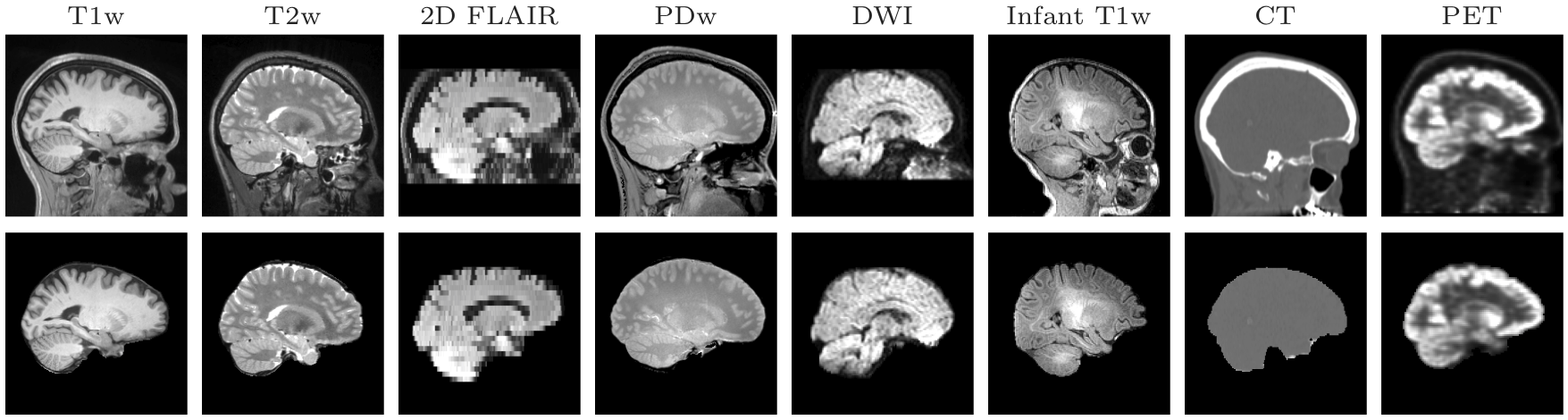
Overview
SynthStrip is a skull-stripping tool that extracts brain voxels from a landscape of image types, ranging across imaging modalities, resolutions, and subject populations. It leverages a deep learning strategy to synthesize arbitrary training images from segmentation maps, yielding a robust model agnostic to acquisition specifics.
If you use the tool or dataset, please cite SynthStrip (BibTeX):
SynthStrip: Skull-Stripping for Any Brain Image
Andrew Hoopes, Jocelyn S. Mora, Adrian V. Dalca, Bruce Fischl*, Malte Hoffmann* (*equal contribution)
NeuroImage 260, 2022, 119474
Boosting skull-stripping performance for pediatric brain images
William Kelley, Nathan Ngo, Adrian V. Dalca, Bruce Fischl, Lilla Zöllei*, Malte Hoffmann* (*equal contribution)
IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2024, forthcoming

SynthStrip Dataset
The SynthStrip data are a collection of full-head images with corresponding ground-truth brain masks from 622 MRI, CT, and PET scans. We include label maps for 131 adult MPRAGE scans, with standard FreeSurfer brain labels and additional non-brain labels. The images span various MRI contrasts, resolutions, and populations ranging from infants to glioblastoma patients. While we cannot redistribute the CT and PET data, we provide information on how to obtain these. The 2D subset consists of sagittal slices extracted from each file in the 3D dataset.
See README for dataset information and license
Download the 3D SynthStrip dataset (v1.5, 6.9 GB)
Download the 2D SynthStrip dataset (v1.5, 39 MB)
Verify download integrity with SHA-256 checksums
Download, verify, and extract the data with:
curl -O https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/docs/synthstrip/data/SHA256
curl -O https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/docs/synthstrip/data/synthstrip_data_v1.5.tar
curl -O https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/docs/synthstrip/data/synthstrip_data_v1.5_2d.tar
shasum -c SHA256
tar -xf synthstrip_data_v1.5.tar
tar -xf synthstrip_data_v1.5_2d.tarIf you use these data, please cite SynthStrip (BibTeX).
SynthStrip Tool
We ship SynthStrip as a command-line tool with FreeSurfer and as a standalone utility using Docker or Singularity containers. Both versions are functionally identical and use the same command-line syntax.
Within FreeSurfer: The mri_synthstrip utility has been included in FreeSurfer since the v7.3.0 release. For the most up-to-date version of SynthStrip, please download a build of the FreeSurfer development branch.
Containerized version: If you do not want to install FreeSurfer, you can run SynthStrip in a container. We provide a script that wraps the container, so you do not need to worry about mounting input and output directories. For those interested, the underlying build image is available on the Docker Hub.
Singularity: Download the Singularity-based wrapper script with:
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freesurfer/freesurfer/dev/mri_synthstrip/synthstrip-singularity && chmod +x synthstrip-singularityDocker: Download the Docker-based wrapper script with:
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freesurfer/freesurfer/dev/mri_synthstrip/synthstrip-docker && chmod +x synthstrip-dockerPlease read the brief instructions at the top of the downloaded script. Singularity requires one-time configuration.
Usage
Once installed, you can run SynthStrip with the following syntax, where "stripped.nii.gz" is a skull-stripped version of the input image "input.nii.gz".
mri_synthstrip -i input.nii.gz -o stripped.nii.gzNote: For the container version, replace mri_synthstrip with the wrapper script name (e.g. synthstrip-singularity).
Use the -m flag to save a binary brain mask:
mri_synthstrip -i input.mgz -o stripped.mgz -m mask.mgzIf you would like to compute the immediate boundary of the brain excluding surrounding CSF, use the --no-csf flag. You may also want to explore the -b option, which controls the boundary distance from the brain.
mri_synthstrip -i input.nii -o stripped.nii --no-csfDisplay additional options with the --help flag. SynthStrip should take less than 1 minute on the CPU for most images with voxel sizes near 1 mm3. As image size or resolution increases, the runtime might increase as well.
Video (5 minutes)
Code and Weights
Should you wish to set up a custom Python environment, you can access the SynthStrip scripts in the FreeSurfer repository on GitHub and download the weight files independently:
- the main SynthStrip model (version 1, 29 MB)
- a model for predicting brain masks without CSF (version 1, 29 MB)
- a preliminary d-SynthStrip model for pediatric brain masks without CSF (version 1, 29 MB)
We also export the Python requirements used to build the latest SynthStrip container.
Solved Issues
Previous versions may have shifted NIfTI outputs during visualization (issue 1025), generated an error indicating that "ITK only supports orthonormal direction cosines" (issue 1015), or introduced floating-point errors in output voxel sizes (issue 1060). These problems were related to improper qform and sform handling by the surfa library and have been fixed in FreeSurfer releases after 2023-02-14 and in SynthStrip container v1.4. Make sure to update the wrapper script headers!
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Douglas Greve, Lilla Zöllei, and David Salat for sharing data. This research project benefitted from computational hardware generously provided by the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center.