| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 9: | Line 9: |
|
|
|
| Line 12: | Line 10: |
| Line 18: | Line 15: |
| Line 21: | Line 17: |
| Right and left labels for entorhinal are available in freesurfer 5.3 | Right and left labels for entorhinal are available in freesurfer 5.3 and 6.0+. |
| Line 23: | Line 19: |
| The labels are in freesurfer surface space and located in subjects dir subj/label/?h.entorhinal_exvivo.label | The labels are in freesurfer surface space and located in subjects dir {{{subj/label/?h.entorhinal_exvivo.label}}}. They are generated by default by {{{recon-all -all}}, but can be regenerated with the {{{recon-all -ba-labels}}} flag. |
| Line 25: | Line 21: |
| See instructions on how to view in freeview | In freeview, after loading a surface, the label can be viewed either by loading the Annotation file {{{subj/label/?h.BA_exvivo.annot}}}, or by loading the Label file {{{?h.entorhinal_exvivo.label}}} (which allows selection of 'Heat Scale' viewing mode to display the probability mapping), or by loading the Label file {{{?h.entorhinal_exvivo.thresh.label}}}, which is a thresholded version, more suitable as an ROI. |
| Line 27: | Line 23: |
| To generate stats on this label (../stats/$hemi.BA.stats) |
Stats on this label are found in {{{subj/stats/?h.BA_exvivo.stats}}} See also [[BrodmannAreaMaps]] and [[Perirhinal]]. |
Entorhinal Cortex
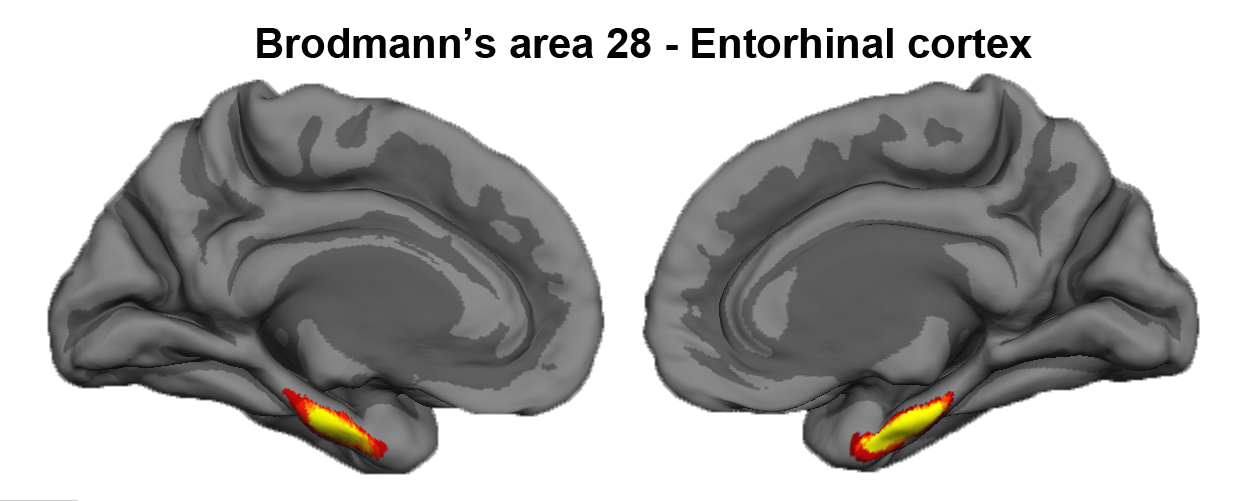
Author: Jean Augustinack
The entorhinal cortex is located on the crown of the anterior parahippocampal gyrus. Brodmann assigned the number 28 to entorhinal cortex (Brodmann’s area 28). Entorhinal cortex displays a unique cytoarchitecture with large neurons in layer II that form clusters. The entorhinal cortex is the gateway to the hippocampus. In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), neurons in the entorhinal cortex, particularly those in layer II, begin to die and some leave behind a pathological marker – the neurofibrillary tangle. Neurofibrillary tangles and significant cell death characterize the neuronal loss in AD where neurofibrillary tangles and subsequent atrophy have been correlated with dementia.
Please note that there two entorhinal labels exist in FreeSurfer 1) the EC label included in the aparc atlas and 2) the cytoarchitecturally-defined entorhinal label (i.e., the ex vivo one).
Reference for Entorhinal cortex, Cytoarchitecturally-defined labels:
Fischl B, et al. Predicting the location of entorhinal cortex from MRI. Neuroimage. 2009 Aug 1;47(1):8-17.
Where to find the entorhinal (cytoarchitectural-defined) labels in FreeSurfer
Right and left labels for entorhinal are available in freesurfer 5.3 and 6.0+.
The labels are in freesurfer surface space and located in subjects dir subj/label/?h.entorhinal_exvivo.label. They are generated by default by recon-all -all}}, but can be regenerated with the {{{recon-all -ba-labels flag.
In freeview, after loading a surface, the label can be viewed either by loading the Annotation file subj/label/?h.BA_exvivo.annot, or by loading the Label file ?h.entorhinal_exvivo.label (which allows selection of 'Heat Scale' viewing mode to display the probability mapping), or by loading the Label file ?h.entorhinal_exvivo.thresh.label, which is a thresholded version, more suitable as an ROI.
Stats on this label are found in subj/stats/?h.BA_exvivo.stats
See also BrodmannAreaMaps and Perirhinal.
