Up to FreeviewGuide |
Back to FreeviewAnatomicalVolumes |
Continue to FreeviewManualTransformation |
Segmentation
Setup
Once freeview is running, the first thing the user will need to do is to load the volume which they wish to segment. This can be done by clicking the Load Volume button  . The button is a profile view of a face with a green plus sign, located second from the left in the toolbar directly below the 'Volumes' tab on the left side of the screen. Once the desired volume is chosen, it will load and appear visible in the black visual screens in Freeview. Make sure the Color map is set to'Grayscale.'
. The button is a profile view of a face with a green plus sign, located second from the left in the toolbar directly below the 'Volumes' tab on the left side of the screen. Once the desired volume is chosen, it will load and appear visible in the black visual screens in Freeview. Make sure the Color map is set to'Grayscale.'
Once the original volume is loaded, a second one needs to be created to do segmentations on. This can be done by clicking the New Volume button, directly to the left of the Load Volume button  . A new window will pop up, allowing the user to choose a name for the new volume; in this same pop-up window, Select Template Volume must be chosen to match the original volume loaded. Once created, the new volume will appear. It's Color map needs to be changed from Grayscale to Lookup Table in order to begin segmentation (visual screen will remain black until this is done).
. A new window will pop up, allowing the user to choose a name for the new volume; in this same pop-up window, Select Template Volume must be chosen to match the original volume loaded. Once created, the new volume will appear. It's Color map needs to be changed from Grayscale to Lookup Table in order to begin segmentation (visual screen will remain black until this is done).
Segmenting
Freeview is comprised of a number of drawing and visualizing tools that are intended to help the user manually segment, or outline, brain structures.
To begin segmentation, the drawing button must be selected. This button is located third from the left in the topmost toolbar, and appears to be a sagittal view of a face with a pencil drawn over it. Once this is selected, a seperate window called Voxel Edit will appear. This box allows users to select the tools with which they wish to segment the volume.
Regardless of tool being used, the first thing to do is select the desired color corresponding to the area that is being segmented. The colors and their respective areas are in the lower left corner of the window.
Freehand
The Freehand tool is used to outline structures that must be drawn by hand by adding or deleting individual voxels. This tool is generally used for structures that have similar intensity values as bordering tissue. The default brush size is one, which means the user will be able to edit one voxel at a time. This is good for precise lines and smaller outlines. To make the brush size larger, simply change the value in 'Brush size.' It is helpful to manually draw the outline of a structure using the Freehand tool, and then fill in the outline using the Fill button.
Fill
The Fill button allows users to color in any outlined area. As a shortcut to the 'Fill' button, the user can hold control on the keyboard while still in 'Freehand' mode - the mouse will change from a pencil to a 'Fill' icon (bucket of paint). While holding control, the user can click anywhere inside the drawn outline to fill it in. Be Careful - if the desired area is not completely enclosed by the outline, filling it in can color the entire screen. If this happens, simply press Ctrl + Z - this is the undo button and can always be used to undo the last action. If the Fill button is not filling in the enclosed areas as desired, it is because its tolerance is set too low. This means that the 'Fill' tool will only color voxels within the enclosed area that are of similar intensity (color) value to the voxel selected. The default tolerance is zero, which means only voxels with intensities equivalent to the intensity of the voxel selected will be filled in using the fill tool. To change the tolerance, go to the Voxel Edit window (which should be up on your screen). Click the 'Fill' icon, which is the fourth from the left along the topmost toolbar. User can change to desired tolerance from here.
Dot Connector
The Dot Connector tool is the second icon from the left along the topmost toolbar of the 'Voxel Edit' window ![]() . This tool is a useful alternative to freehand, especially when dealing with structures with relatively flat edges. Once selected, it allows the user to start a line by left clicking with the mouse. A thin red line will appear, and the user can drag the endpoint to a desired location and set it by clicking the left mouse button again. The thin red line will become a straight drawn line (of selected color value) and the endpoint will become a new beginning point for the next connection. To stop using this tool, right click anywhere on the screen.
. This tool is a useful alternative to freehand, especially when dealing with structures with relatively flat edges. Once selected, it allows the user to start a line by left clicking with the mouse. A thin red line will appear, and the user can drag the endpoint to a desired location and set it by clicking the left mouse button again. The thin red line will become a straight drawn line (of selected color value) and the endpoint will become a new beginning point for the next connection. To stop using this tool, right click anywhere on the screen.
Intensity Sensor Line
The Intensity Sensor Line tool is located third from the left along the topmost toolbar of the 'Voxel Edit' window ![]() . This Tool allows the user to create lines in a similar fashion to the Dot Connector tool. Similarly, once the tool is selected, clicking a startpoint will prompt a thin red line to appear. However, the user will notice that this line will automatically stay along the dividing line between two areas of different intensity. Because of this, this tool is really only useful for borders with high contrast, such as grey or white matter and cerebrospinal fluid. To finalize the line, the user simply left clicks again once the red line has taken desired shape. The endpoint will become a new begininng point. Right click with the mouse to stop using the tool.
. This Tool allows the user to create lines in a similar fashion to the Dot Connector tool. Similarly, once the tool is selected, clicking a startpoint will prompt a thin red line to appear. However, the user will notice that this line will automatically stay along the dividing line between two areas of different intensity. Because of this, this tool is really only useful for borders with high contrast, such as grey or white matter and cerebrospinal fluid. To finalize the line, the user simply left clicks again once the red line has taken desired shape. The endpoint will become a new begininng point. Right click with the mouse to stop using the tool.
Intensity Contour
The Intensity Contour tool is used to estimate borders between areas of varying intensity. It is most useful for drawing borders between tissue types with high contrast, such as grey or white matter and cerebrospinal fluid. Specifically, this tool works well to highlight the exterior border of the cerebral hemispheres and lateral ventricles. To use the tool, click on the “intensity contour” button in the drawing toolbox, and then drag the mouse while holding down the “Ctrl” and “Alt” buttons until you reach the best fit outline of your structure of interest. Then, edit the outline using shift + right click to add voxels, or right click to delete. Make sure that you outline the entire structure and fill in any holes. Finally, fill it in with the appropriate label by holding down “Ctrl” while left-clicking. Turn the intensity contour on and off by clicking “Alt” + “H”.
Useful Shortcuts and Tools
To erase, hold down the shift key and left click over any voxels that are to have their color reset.
'Ctrl + Z' will undo the last action.
'Alt + L' allows user to toggle between seeing only the outlines of labels vs. the entire filled in area.
'Up Key" and 'Down Key" are used to move forward and backward through slices (NOTE: If you are using an older version of FreeSurfer then 'Page Up' and 'Page Down' are used to move forward or backward through slices) in the plane whose screen the mouse is in. For example, even if the coronal view is on the large screen, if the mouse is in the axial view's screen, 'Up Key' and 'Down Key' will move through axial slices, and the coronal slice will not change.
'Ctrl + Shift + Left mouse' moves the cursor to the voxel where the user clicked when in Voxel Edit mode.
'Ctrl + Left mouse' allows user to fill in outlined area without changing tool to 'Fill' in Voxel Edit window.
'Shift + C' while in the Freehand mode of Voxel edit switches to the Color picker mode. The user can then click a label, and the brush value will change to this. After the value has changed, the cursor returns to Freehand mode.
Views
Freeview allows users to work in either a sagittal, axial or coronal view. To switch between these, just click the desired view between the three buttons in the center of the topmost toolbar (if the mouse is held over the buttons, a small text box telling which view the button is for will pop up). The user also has the ability to look at all views at the same time with several different orientations. In the case that all four views are up simultaneously, the selected view will appear in the main screen.
Besides just looking at the labels, there are two other ways of inspecting the segmentations.
* You can use label outline only to view the segmentation labels by only the label outlines. This can be useful if you have a structural volume also loaded and want to inspect the underlying intensity values / anatomies.
* You can use Show isosurface in 3D view. That option will create a surface from the segmentation labels and you will be able to view the result in the "3D model view". You can make this view the principal one by hitting ALT+3 simultaneously.
Segmenting using a Cintiq tablet or display
- Mac Setup
Under system preferences click on 'wacom tablet' and then 'grip pen' to configure the pen button functions. For ease of use you can program each of the two buttons on the pen as both 'modifiers' the bottom one as the shift key and the top one as the CTRL key. That way when you outline a structure you can press the top key and tap inside the outline to fill. Additionally, when you're in the "navigate" menu in freeview you can hold down the buttom key and move the pen around as you would the mouse to adjust the contrast. Lastly, if you draw voxels you don't want you can click the bottom key and redraw over them to delete.
After you've programmed the pen, click on 'functions' to program the side buttons. for each one click 'keystroke' and click in the box to type whatever combination of keys you would like to activate. You must then enter something as the 'name' in order to save it. Good functions to program would be CTRL+Z for "undo." You must then name it undo and save. You can also program 'Up Key' save it, and then for the next 'Down Key'. this way you can scroll through the volume without a keyboard. It may also be helpful to program things like copy and paste. By programming all the keys in this way, you may use the cintiq completely without keyboard or mouse.
- Linux (CentOS 6) Setup
Command-line:'xsetwacom' allows you to configure the buttons for wacom devices from the command-line, although the button naming scheme it uses is not quite intuitive. Any xsetwacom commands you use will be user-specific and will need to be saved somewhere, ideally in the .cshrc or as an alias the user can run.
example commands for setting stylus buttons
xsetwacom --set "Wacom Cintiq 21UX2 stylus" Button 2 "key shift"
xsetwacom --set "Wacom Cintiq 21UX2 stylus" Button 3 "key control"
xsetwacom help
Usage: xsetwacom [options] [command [arguments...]] Options: -h, --help - usage -v, --verbose - verbose output -V, --version - version info -d, --display "display" - override default display -s, --shell - generate shell commands for 'get' -x, --xconf - generate xorg.conf lines for 'get' Commands: --list devices - display detected devices --list parameters - display supported parameters --list modifiers - display supported modifier and specific keys for keystrokes --set "device name" parameter [values...] - set device parameter by name --get "device name" parameter [param...] - get current device parameter(s) value by name
GUI (graphical user interface): On CentOS 6 you should be able to configure all the buttons (except the buttons on the stylus) by just going to System->Preferences->Wacom Tablet which runs a GUI called 'gnome-wacom-properties'. To set the stylus buttons to key combinations which are not available in the drop-down menu in the GUI, you will have to use the xsetwacom command-line. Below is a snapshot of a typical button setup for the Wacom Cintiq 21UX.
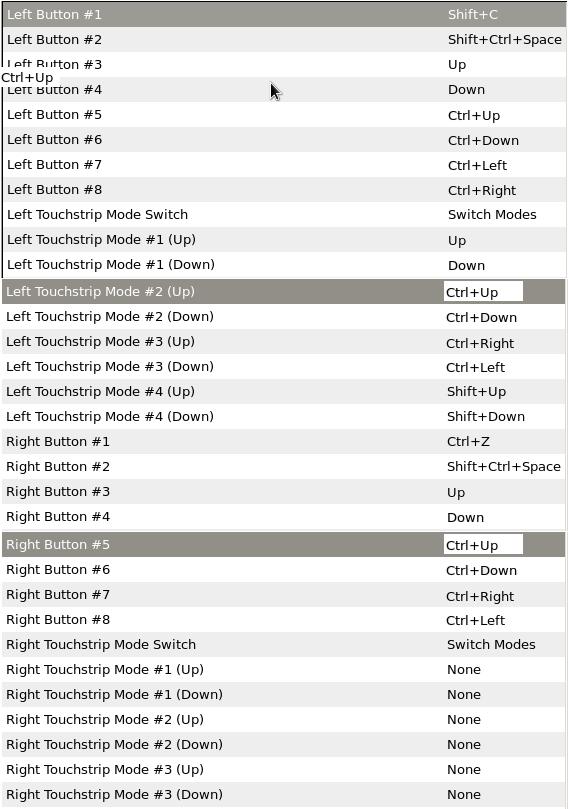
- Hints
When using a smaller tablet to segment, CTRL+P is a helpful shortcut which makes the side menu disappear and reappear, allowing you more space to view the brain. Additionally, there is a small track pad on the side of most Cintiq tablets which will zoom in and out on the volume when you run your finger along it.
