Correcting Pial Surfaces
To follow this exercise exactly be sure you've downloaded the tutorial data set before you begin. If you choose not to download the data set you can follow these instructions on your own data, but you will have to substitute your own specific paths and subject names.
The pial surface is created by expanding the white matter surface so that it closely follows the gray-CSF intensity gradient as found in the brainmask.mgz volume. Once an accurate white surface is created then you can work on correcting the pial surface if needed. The pial surface boundary and white matter surface boundary should not cross. After the pial surface has been generated, it's a good idea to visually check it for defects that may have been created during automatic topology fixing. To check the pial surface, it may be loaded into freeview and viewed along with the brainmask.mgz volume. If the surface appears not to follow the gray-CSF boundary in the volume, edits may be required.
Editing the Volume
Subject pial_edits_before is an example of the pial surface including non-cortex within the boundaries. This page will take you through fixing this and other similar problems with the pial surface including non-cortex material. First, make sure you have pial_edits_before loaded in freeview:
freeview -v cp_before/mri/brainmask.mgz \ -f cp_before/surf/lh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ cp_before/surf/lh.pial:edgecolor=red \ cp_before/surf/rh.white:edgecolor=yellow \ cp_before/surf/rh.pial:edgecolor=red \
Use the 'page up' and 'page down' keys to go through the volume slice by slice, and view the pial surface (red line) and white matter surface (yellow line). Notice the bright diagonal line in slice 157 that has caused the pial surface to expand past the actual pial boundary. This is the result of a bad segmentation incorporating a piece of the dura within the pial surface.
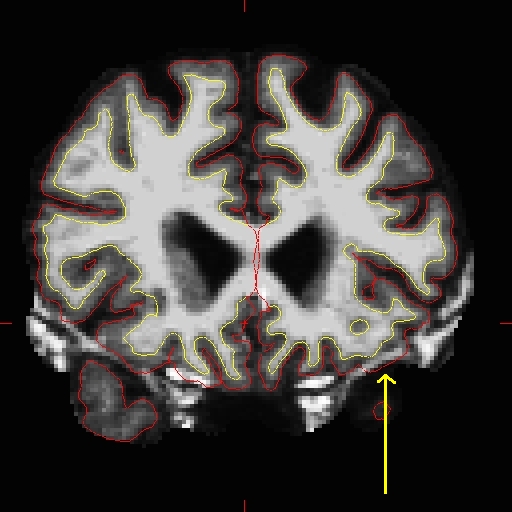
To fix this type of error you can simply edit away the offending voxels from the brainmask.mgz volume. To do this you will need to click on the voxel button  and this window will pop up:
and this window will pop up:
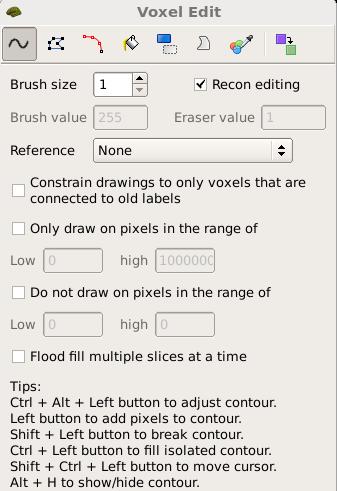
First, set the brush to a size comfortable for you. A brush size of 2 works well for this edit. Next, click the 'Recon editing' check box so that the Brush value and Eraser value set to 255 and 1, respectively. Make sure the first option "freehand", at the top, is selected and you're ready to make your edits. Find a place in the image where the dura is causing errors in the segmentation. Double check that the brainmask.mgz is selected and highlighted and not the T1.mgz, as you are only making edits to the brainmask. Hold down the shift key and use the left mouse button to delete the voxels. It is not necessary to completely remove the dura to get an adequate pial surface, but it is good to do so until you are more familiar with manual editing. When you are finished removing the bright diagonal line in slice 157, it should look like this:
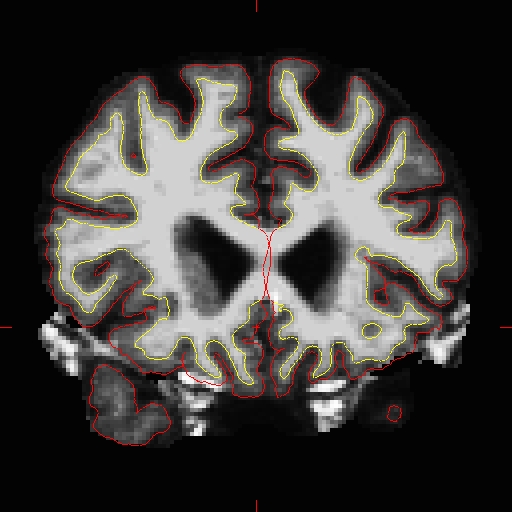
Continue on the other slices until the dura is removed. Ctrl-z and the 'Undo' button  at the top in freeview allows you to go back and undo as many edits as you like.
at the top in freeview allows you to go back and undo as many edits as you like.
At any time, you can save the changes you've made to the brainmask.mgz volume by selecting 'Save Volume' in freeview's 'File' menu or by clicking the 'Save Volume'  button. Make sure the brainmask.mgz is the one highlighted while saving if you have the T1.mgz open at the same time. You can check your result by viewing the brainmask.mgz volume in the pial_edits_after directory.
button. Make sure the brainmask.mgz is the one highlighted while saving if you have the T1.mgz open at the same time. You can check your result by viewing the brainmask.mgz volume in the pial_edits_after directory.
Regenerating the Surface
When you are finished editing the voxels, you will need to regenerate the surfaces. Since the white matter hasn't been changed, you don't need to resegment the volume. You can regenerate the pial surface with:
recon-all -autorecon-pial -subjid pial_edits_before
Do not run this command if you are conducting the tutorial! This step will take a long time and there is no need to run it for the tutorial purposes.
Edits to correct pial surface extension into cerebellum
The brain.finalsurfs.manedit.mgz volume will allow for the correction of a particular type of problem involving pial surface misplacement whereby parts of the pial surface have extended into the cerebellum in certain areas. It is only in this case where the pial surface extends into cerebellum where the brain.finalsurfs.manedit.mgz volume should be edited. For all other non-cerebellum pial surface problems, brainmask.mgz should be edited. This cerebellum / pial surface problem can be fixed by removing those cerebellum voxels and other surrounding problematic voxels in the brain.finalsurfs.manedit.mgz volume such that upon running recon-all, the pial surface will be pulled in as desired, bordering only gray matter/ CSF boundary, and not jutting into the cerebellum. If only edits to this volume are made on a subject, it is sufficient to re-run recon-all from the point of these edits using the flag -autorecon3-pial. Note that you must create brain.finalsurfs.manedit.mgz by copying it from brain.finalsurfs.mgz:
cd <subjid>/mri cp brain.finalsurfs.mgz brain.finalsurfs.manedit.mgz
You do not need to do this for this tutorial. If you're interested, please refer to the brain.finalsurfs section on the Longitudinal Tutorial here.
